
[c][explained] Demystifying Pointers — Function Pointers
Find the complete program on https://www.notion.so/theteachr/Function-Pointers-9848de630cae47a7ad1ca5552d23a66d.
From playlist Demystifying Pointers
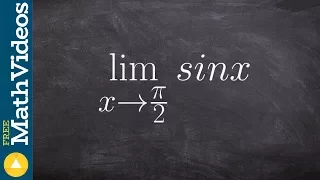
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

Using trig limits to evaluate the limit
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

Use limit laws and special trig limits to evaluate
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

How to use special trig limits to evaluate the limit
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

How to evaluate the special trig limit with sine and fractions
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

Logic 4: Natural Deduction with Logical Axioms — Tutorial 4/4
In this four-part series we explore propositional logic, Karnaugh maps, implications and fallacies, predicate logic, existential and universal quantifiers and finally natural deduction. Become a member: https://youtube.com/Bisqwit/join My links: Twitter: https://twitter.com/RealBisqwit L
From playlist Logic Tutorial
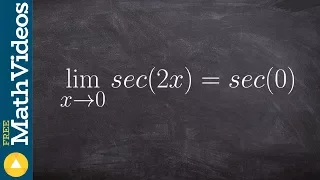
How to evaluate a limit with secant
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

Toward an imaginary Ax-Kochen-Ershov principle - S. Rideau - Workshop 2 - CEB T1 2018
Silvain Rideau (CNRS – Université Paris Diderot) / 09.03.2018 Toward an imaginary Ax-Kochen-Ershov principle. All imaginaries that have been classified in Henselian fields (possibly with operators) have been shown to be geometric in the sense of Haskell-HrushovskiMacpherson. In general,
From playlist 2018 - T1 - Model Theory, Combinatorics and Valued fields

Foundations - Seminar 13 - Gödel's incompleteness theorem Part 5
Billy Price and Will Troiani present a series of seminars on foundations of mathematics. In this seminar Will Troiani continues with the proof of Gödel's incompleteness theorem. You can join this seminar from anywhere, on any device, at https://www.metauni.org. This video was filmed in D
From playlist Foundations seminar
Getting the Most from Algebraic Solvers in Mathematica
This talk by Adam Strzebonski at the Wolfram Technology Conference 2011 gives a survey of Mathematica functions related to solving algebraic equations and inequalities. It also discusses the choice of the most appropriate solvers for various types of problems and the ways of formulating th
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2011

Elliot Kaplan, McMaster Unviersity
October 7, Elliot Kaplan, McMaster Unviersity Generic derivations on o-minimal structures
From playlist Fall 2021 Online Kolchin Seminar in Differential Algebra

Logic 9 - First Order Resolution | Stanford CS221: AI (Autumn 2021)
For more information about Stanford's Artificial Intelligence professional and graduate programs visit: https://stanford.io/ai Associate Professor Percy Liang Associate Professor of Computer Science and Statistics (courtesy) https://profiles.stanford.edu/percy-liang Assistant Professor
From playlist Stanford CS221: Artificial Intelligence: Principles and Techniques | Autumn 2021

Can p-adic integrals be computed? - Thomas Hales
Automorphic Forms Thomas Hales April 6, 2001 Concepts, Techniques, Applications and Influence April 4, 2001 - April 7, 2001 Support for this conference was provided by the National Science Foundation Conference Page: https://www.math.ias.edu/conf-automorphicforms Conference Agena: ht
From playlist Mathematics

Evaluating the limit using properties of limits and special trig limits
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig
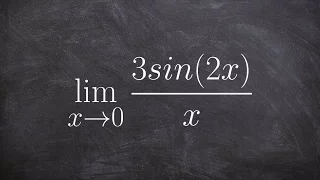
Learn how to use special trig limits to evaluate
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig
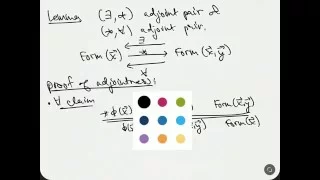
Model Theory - part 06 - Quantifiers as Adjoints
In this video we start to talk about how one can view quantifiers as adjoints of certain functors.
From playlist Model Theory
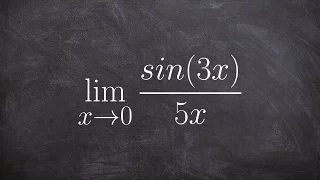
Evaluating using special trig limits
👉 Learn how to evaluate the limit of a function involving trigonometric expressions. The limit of a function as the input variable of the function tends to a number/value is the number/value which the function approaches at that time. The limit of a function is usually evaluated by direct
From playlist Evaluate Limits with Trig

Multi-valued algebraically closed fields are NTP₂ - W. Johnson - Workshop 2 - CEB T1 2018
Will Johnson (Niantic) / 05.03.2018 Multi-valued algebraically closed fields are NTP₂. Consider the expansion of an algebraically closed field K by 𝑛 arbitrary valuation rings (encoded as unary predicates). We show that the resulting structure does not have the second tree property, and
From playlist 2018 - T1 - Model Theory, Combinatorics and Valued fields
