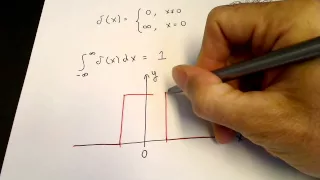Measure theory | Fourier analysis | Generalized functions
Dirac delta function
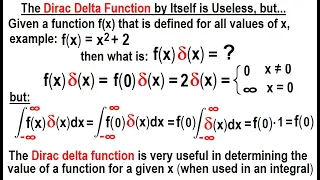
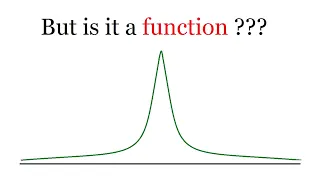
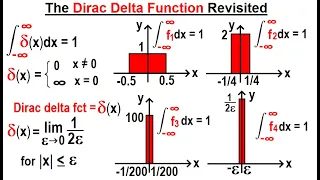
In mathematics, the Dirac delta distribution (δ distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. The current understanding of the unit impulse is as a linear functional that maps every continuous function (e.g., ) to its value at zero of its domain, or as the weak limit of a sequence of bump functions (e.g., ), which are zero over most of the real line, with a tall spike at the origin. Bump functions are thus sometimes called "approximate" or "nascent" delta distributions. The delta function was introduced by physicist Paul Dirac as a tool for the normalization of state vectors. It also has uses in probability theory and signal processing. Its validity was disputed until Laurent Schwartz developed the theory of distributions where it is defined as a linear form acting on functions. The Kronecker delta function, which is usually defined on a discrete domain and takes values 0 and 1, is the discrete analog of the Dirac delta function. (Wikipedia).