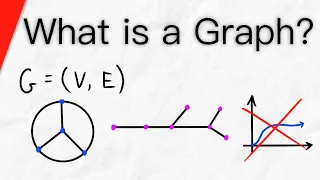Graph theory
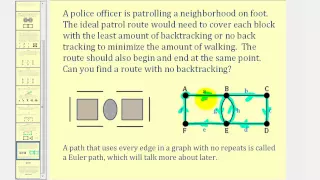
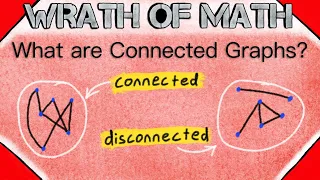
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices (also called nodes or points) which are connected by edges (also called links or lines). A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically. Graphs are one of the principal objects of study in discrete mathematics. (Wikipedia).