
Isolated Vertex - Graph Theory
Example and explanation of an isolated vertex
From playlist Graph Theory
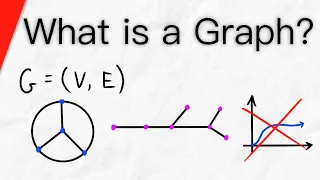
What is a Graph? | Graph Theory
What is a graph? A graph theory graph, in particular, is the subject of discussion today. In graph theory, a graph is an ordered pair consisting of a vertex set, then an edge set. Graphs are often represented as diagrams, with dots representing vertices, and lines representing edges. Each
From playlist Graph Theory

Extremal theory of ordered graphs – Gábor Tardos – ICM2018
Combinatorics Invited Lecture 13.3 Extremal theory of ordered graphs Gábor Tardos Abstract: We call simple graphs with a linear order on the vertices ‘ordered graphs’. Turán-type extremal graph theory naturally extends to ordered graphs. This is a survey on the ongoing research in the ex
From playlist Combinatorics

Overview of Loops in Graph Theory | Graph Loop, Multigraphs, Pseudographs
What are loops in graph theory? Sometimes called self loops, a loop in a graph is an edge that connects a vertex to itself. These are not allowed in what are often called "simple graphs", which are the graphs we usually study when we begin studying graph theory. In simple graphs, loop ed
From playlist Graph Theory
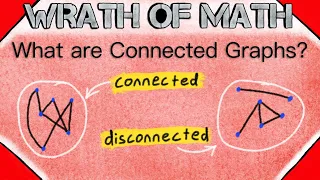
What are Connected Graphs? | Graph Theory
What is a connected graph in graph theory? That is the subject of today's math lesson! A connected graph is a graph in which every pair of vertices is connected, which means there exists a path in the graph with those vertices as endpoints. We can think of it this way: if, by traveling acr
From playlist Graph Theory

Graph Theory: 03. Examples of Graphs
We provide some basic examples of graphs in Graph Theory. This video will help you to get familiar with the notation and what it represents. We also discuss the idea of adjacent vertices and edges. --An introduction to Graph Theory by Dr. Sarada Herke. Links to the related videos: https
From playlist Graph Theory part-1

Dieter Rautenbach: Restricted types of matchings
Abstract: We present new results concerning restricted types of matchings such as uniquely restricted matchings and acyclic matchings, and we also consider the corresponding edge coloring notions. Our focus lies on bounds, exact and approximative algorithms. Furthermore, we discuss some ma
From playlist Combinatorics
Tree Graphs - Intro to Algorithms
This video is part of an online course, Intro to Algorithms. Check out the course here: https://www.udacity.com/course/cs215.
From playlist Introduction to Algorithms

Additive combinatorics through the lens of communication complexity - Toniann Pitassi
Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics Seminar II Topic: Additive combinatorics through the lens of communication complexity Speaker: Toniann Pitassi Affiliation: University of Toronto and Columbia University; Visiting Professor, School of Mathematics Date: November 15, 2022 In this tal
From playlist Mathematics

Limits of permutation sequences - Yoshi Kohayakawa
Conference on Graphs and Analysis Yoshi Kohayakawa June 5, 2012 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Graph Theory: 02. Definition of a Graph
In this video we formally define what a graph is in Graph Theory and explain the concept with an example. In this introductory video, no previous knowledge of Graph Theory will be assumed. --An introduction to Graph Theory by Dr. Sarada Herke. This video is a remake of the "02. Definitio
From playlist Graph Theory part-1

Nathalie Aubrun: Subshifts, the emptiness problem and Lovász local lemma
HYBRID EVENT Subshifts are set of colorings of a group by a finite alphabet that respect local constraints, given by some forbidden patterns ode m. The asymmetric version of Lovász local lemma reveals particularly useful to prove the existence of a coloring inside a subshift, i.e. a colori
From playlist Combinatorics

Maria CHUDNOVKY - Induced subgraphs and tree decompositions
https://ams-ems-smf2022.inviteo.fr/
From playlist International Meeting 2022 AMS-EMS-SMF
From playlist Plenary talks One World Symposium 2020

Weakly Connected Directed Graphs | Digraph Theory
What is a connected digraph? When we start considering directed graphs, we have to rethink our definition of connected. We say that an undirected graph is connected if there exists a path connecting every pair of vertices. However, in a directed graph, we need to be more specific since it
From playlist Graph Theory

A formal definition of a Graph and its properties
From playlist Graph Theory

Andreas Thom: Asymptotics of Cheeger constants and unitarisability of groups
Talk by Andreas Thom in Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Europe) http://www.noncommutativegeometry.nl/ncgseminar/ on January 26, 2021
From playlist Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Europe)

Monique Laurent: Combinatorial and algorithmic properties of Robinsonian matrices
Abstract: Robinsonian matrices are structured matrices that have been introduced in the 1950's by the archeologist W.S. Robinson for chronological dating of Egyptian graves. A symmetric matrix is said to be Robinsonian if its rows and columns can be simultaneously reordered in such a way t
From playlist Combinatorics
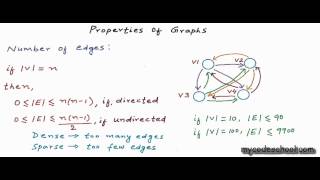
Data structures: Properties of Graphs
See complete series on data structures here: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL2_aWCzGMAwI3W_JlcBbtYTwiQSsOTa6P In this lesson, we have described below properties of Graph data structure: a) directed graph vs undirected graph b) weighted graph vs unweighted graph c) sparse graph vs
From playlist Data structures

Using networks to detect dynamical regime change in time series by Michael Small
PROGRAM DYNAMICS OF COMPLEX SYSTEMS 2018 ORGANIZERS Amit Apte, Soumitro Banerjee, Pranay Goel, Partha Guha, Neelima Gupte, Govindan Rangarajan and Somdatta Sinha DATE: 16 June 2018 to 30 June 2018 VENUE: Ramanujan hall for Summer School held from 16 - 25 June, 2018; Madhava hall for W
From playlist Dynamics of Complex systems 2018