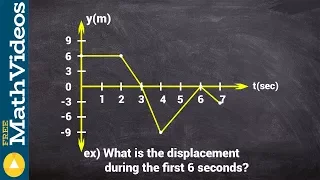
What is the displacement of a particle from a position graph
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

Learn how to determine when a particle is at rest using a calculator
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

Determine when a particle is moving down from a position graph
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems
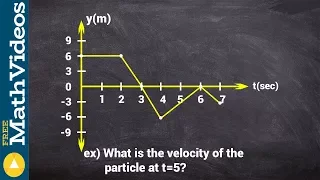
What is the velocity of the particle at a given time from graph
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

Learn how to determine the position when the particle is at rest calculator
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

Determine when a particle is increasing
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

How to determine when a particle is moving to the left and right
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

How to determine the displacement of a particle from a table
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems
Statistical Rethinking - Lecture 12
Lecture 12 - MCMC / Maximum Entropy - Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with R Examples
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Winter 2015

8.01x - Module 08.04 - Resistive Forces, Air Drag, Liquids, Spherical Objects.
Resistive Forces, Air Drag, Liquids, Spherical Objects.
From playlist 8.01x - MIT Help Sessions

MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms: Linkages, Origami, Polyhedra, Fall 2012 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-849F12 Instructor: Erik Demaine This class covers how the pebble algorithm works with first a proof of the 2k property, and then 2k-3. Generic rigidity and the ru
From playlist MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms, Fall 2012

PV-diagrams and expansion work | Thermodynamics | Physics | Khan Academy
Why work from expansion is the area under the curve of a PV-diagram. Why heat is not a state function and internal energy is a state function. Created by Sal Khan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/thermodynamics/laws-of-thermodynamics/v/proof-u-3-2-pv-or-
From playlist Thermodynamics | Physics | Khan Academy
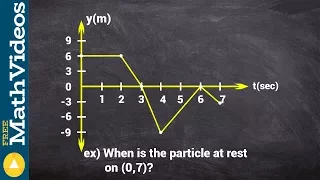
How to find when a particle is at rest from a position graph
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems

Your Daily Equation #9: De Broglie Wavelength
Episode 09 #YourDailyEquation: Particles and waves collide in quantum physics. In today's episode of Your Daily Equation, Brian Greene discusses the famous double slit experiment and explains the formula that connects particles and waves: the DeBroglie wavelength equation. Even if your ma
From playlist Your Daily Equation with Brian Greene

Deeper Combinatorial Lower Bounds - Siu Man Chan
Siu Man Chan Princeton University January 21, 2014 We will discuss space and parallel complexity, ranging from some classical results which motivated the study, to some recent results concerning combinatorial lower bounds in restricted settings. We will highlight some of their connections
From playlist Mathematics

The Controversial Physics of Curling - COLD HARD SCIENCE - Smarter Every Day 111
Patreon Support Link: http://www.patreon.com/smartereveryday Subbable Support Link: http://subbable.com/smartereveryday Tweet this Vid: http://bit.ly/1hf576c Post to FB:http://on.fb.me/1iEpfQ7 Smarter Every Day Infographics are Here: http://smartereveryday.tumblr.com/ Custom Curling Gra
From playlist Smarter Every Day in Order

EEVblog #758 - Pebble Time Smartwatch Unboxing & Review
Dave unboxes and gives his first impressions review of the new Pebble Time Smartwatch. Teardown coming soon... They raised $20M on Kickstarter for this! https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/597507018/pebble-time-awesome-smartwatch-no-compromises Torture test video: https://www.youtube.com/
From playlist Product Reviews & Teardowns

Matter, Mind, & Humanity - General Philosophy (2018 Peter Millican)
In this second lecture, Professor Peter Millican continues the historical introduction to General Philosophy, discussing Matter, Mind, and Humanity, from Descartes to the Present. This comes from a 2018 series on General Philosophy. This series of 8 lectures on General Philosophy was deli
From playlist Philosophy of Mind

MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms: Linkages, Origami, Polyhedra, Fall 2012 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-849F12 Instructor: Erik Demaine This lecture begins with a review of linkages and classifying graphs as generically rigid or flexible. Conditions for minimally ge
From playlist MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms, Fall 2012

When is the particle at rest from a velocity graph
Keywords 👉 Learn how to solve particle motion problems. Particle motion problems are usually modeled using functions. Now, when the function modeling the position of the particle is given with respect to the time, we find the speed function of the particle by differentiating the function
From playlist Particle Motion Problems