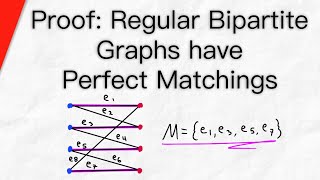
Proof: Regular Bipartite Graph has a Perfect Matching | Graph Theory
An r-regular bipartite graph, with r at least 1, will always have a perfect matching. We prove this result about bipartite matchings in today's graph theory video lesson using Hall's marriage theorem for bipartite matchings. Recall that a perfect matching is a matching that covers every ve
From playlist Graph Theory

Proof: Ore's Theorem for Hamiltonian Graphs | Sufficient Condition for Hamilton Graphs, Graph Theory
What is Ore's Theorem for Hamiltonian graphs and how do we prove it? Ore's Theorem gives us a sufficient condition for a graph to have a Hamiltonian cycle and therefore be a Hamiltonian or Hamilton graph. The theorem tells us that if, in a graph with order n greater than or equal to 3, the
From playlist Graph Theory

Proof: Every Graph has an Even Number of Odd Degree Vertices | Graph Theory
How do we prove that every graph has an even number of odd degree vertices? It seems like a surprising result, how could it be that every graph has such a neat little property? In this video graph theory lesson, we'll prove that every graph has an even number of odd degree vertices, to und
From playlist Graph Theory
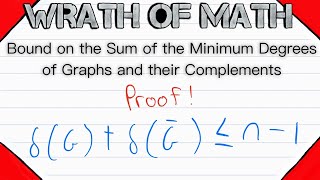
Bound on the Sum of Minimum Degrees of Graphs and their Complements | Graph Theory Proofs
We know the degree of a vertex in a simple graph with n vertices has an upper bound of n-1. The degree of a vertex is n-1 when it is adjacent to every vertex in the graph except for itself (it cannot be adjacent to itself). Then certainly the minimum degree of a graph is less than or equal
From playlist Graph Theory
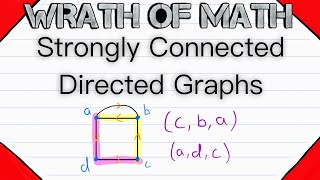
Strongly Connected Directed Graphs | Graph Theory, Digraph Theory
What are strongly connected digraphs? That's what we'll be going over in today's graph theory lesson. We'll recap connectedness, what it means to be weakly connected, and then finish off with the definition of strongly connected! We say a directed graph D is strongly connected if, for eve
From playlist Graph Theory

Proof: Upper Bound for the Size of Planar Graphs | Graph Theory
The size of a planar graph must be less than or equal to three times the number of vertices minus 6. That is, for a planar graph of order n, size m, and with r regions when imbedded in the plane, m is less than or equal to 3n - 6. We'll prove this upper bound for the size of planar graphs
From playlist Graph Theory

Empty Graph, Trivial Graph, and the Null Graph | Graph Theory
Whenever we talk about something that is defined by sets, it is important to consider the empty set and how it fits into the definition. In graph theory, empty sets in the definition of a particular graph can bring on three types/categories of graphs. The empty graphs, the trivial graph, a
From playlist Graph Theory

This continues from our planar graphs video with Maria Chudnovsky at https://youtu.be/xBkTIp6ajAg More links & stuff in full description below ↓↓↓ Four color map theorem (video): https://youtu.be/NgbK43jB4rQ The strong perfect graph theorem (paper): https://arxiv.org/abs/math/0212070 Pr
From playlist Women in Mathematics - Numberphile

Xavier Cabré - 23 September 2016
Cabré, Xavier "The saddle-shaped solution to the Allen-Cahn equation and a conjecture of De Giorgi"
From playlist A Mathematical Tribute to Ennio De Giorgi

Graph Theory: 42. Degree Sequences and Graphical Sequences
Here I describe what a degree sequence is and what makes a sequence graphical. Using some examples I'll describe some obvious necessary conditions (which are not sufficient). Then I explain how a Theorem by Havel and Hakimi gives a necessary and sufficient condition for a sequence of non
From playlist Graph Theory part-8

The Generalized Ramanujan Conjectures and Applications (Lecture 2) by Peter Sarnak
Lecture 2: Thin Groups and Expansion Abstract: Infinite index subgroups of matrix groups like SL(n,Z) which are Zariski dense in SL(n), arise in many geometric and diophantine problems (eg as reflection groups,groups connected with elementary geometry such as integral apollonian packings,
From playlist Generalized Ramanujan Conjectures Applications by Peter Sarnak
MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Spring 2015 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-042JS15 Instructor: Albert R. Meyer License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Spring 2015

An Isoperimetric Inequality for the Hamming Cube and Integrality Gaps in Graphs - Siavosh Benabbas
Siavosh Benabbas Institute for Advanced Study November 21, 2011 In 1970s Paul Erdos asked the following question: Consider all the boolean strings of length n. Assume that one has chosen a subset S of the strings such that no two chosen strings are different in precisely n/4 (or its closes
From playlist Mathematics

The threshold for the square of a Hamilton cycleJinyoung Park
Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics Seminar II Topic: The threshold for the square of a Hamilton cycle Speaker: Jinyoung Park Affiliation: Member, School of Mathematics Date: October 20, 2020 For more video please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics
Proof: Minimum Degree Condition for Connected Graphs | Graph Theory
Let G be a graph of order n, meaning G has n vertices. If the minimum degree of G is greater than or equal to n-1 divided by 2, then G is connected! We prove this sufficient (but not necessary) condition for a graph to be connected in today's video graph theory lesson! To prove the result
From playlist Graph Theory

More designs - P. Keevash - Workshop 1 - CEB T1 2018
Peter Keevash (Oxford) / 01.02.2018 We generalise the existence of combinatorial designs to the setting of subset sums in lattices with coordinates indexed by labelled faces of simplicial complexes. This general framework includes the problem of decomposing hypergraphs with extra edge dat
From playlist 2018 - T1 - Model Theory, Combinatorics and Valued fields

Low-x phenomenology (LXPH - Lecture 3) by Raju Venugopalan
PROGRAM THE MYRIAD COLORFUL WAYS OF UNDERSTANDING EXTREME QCD MATTER ORGANIZERS: Ayan Mukhopadhyay, Sayantan Sharma and Ravindran V DATE: 01 April 2019 to 17 April 2019 VENUE: Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS Bangalore Strongly interacting phases of QCD matter at extreme temperature and
From playlist The Myriad Colorful Ways of Understanding Extreme QCD Matter 2019

Combinatorial methods for PIT (and ranks of matrix spaces) - Roy Meshulam
Optimization, Complexity and Invariant Theory Topic: Combinatorial methods for PIT (and ranks of matrix spaces) Speaker: Roy Meshulam Affiliation: Technion Date: June 8. 2018 For more videos, please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

A Complete Dichotomy Rises from the Capture of Vanishing Signatures - Jin-Yi Cai
Jin-Yi Cai University of Wisconsin November 19, 2012 Holant Problems are a broad framework to describe counting problems. The framework generalizes counting Constraint Satisfaction Problems and partition functions of Graph Homomorphisms. We prove a complexity dichotomy theorem for Holant
From playlist Mathematics

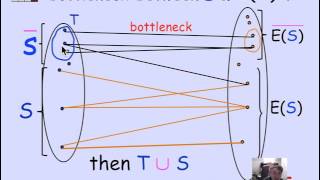
Simple Bounds on Vertex Connectivity | Graph Theory
We know that the vertex connectivity of a graph is the minimum number of vertices that can be deleted to disconnect it or make it trivial. We may then ask, what is an upper bound on the connectivity of a graph? What is a lower bound on the vertex connectivity of a graph? We give the most b
From playlist Graph Theory