
How to determine the domain and range of a quadratic using its vertex
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

How to analyze a quadratic function to graph
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

How to graph a quadratic in vertex form
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

Understanding the discriminant as a part of the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | x^2+bx+c
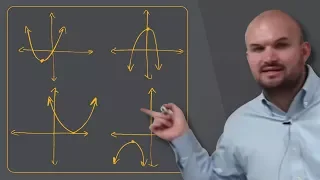
How do the solutions of a quadratic relate to the x intercepts of the graph
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

What are the transformations of vertex form of a quadratic compared to standard form
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

Asymptotics of number fields - Manjul Bhargava [2011]
Asymptotics of number fields Introductory Workshop: Arithmetic Statistics January 31, 2011 - February 04, 2011 January 31, 2011 (11:40 AM PST - 12:40 PM PST) Speaker(s): Manjul Bhargava (Princeton University) Location: MSRI: Simons Auditorium http://www.msri.org/workshops/566
From playlist Number Theory

Johnathan Hanke - Computer-Assisted Proofs in the Arithmetic of Quadratic Forms - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 17 February 2023. Johnathan Hanke of Princeton University presents "Computer-Assisted Proofs in the Arithmetic of Quadratic Forms" at IPAM's Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop. Abstract: Since its early history, the ideas and results in arithmetic of quadratic forms have been inspir
From playlist 2023 Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop

CTNT 2018 - "Arithmetic Statistics" (Lecture 2) by Álvaro Lozano-Robledo
This is lecture 2 of a mini-course on "Arithmetic Statistics", taught by Álvaro Lozano-Robledo, during CTNT 2018, the Connecticut Summer School in Number Theory. For more information about CTNT and other resources and notes, see https://ctnt-summer.math.uconn.edu/
From playlist CTNT 2018 - "Arithmetic Statistics" by Álvaro Lozano-Robledo

What do I need to know to graph a quadratic in vertex form
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

CTNT 2020 - Elliptic curves and the local-global principle for quadratic forms - Asher Auel
The Connecticut Summer School in Number Theory (CTNT) is a summer school in number theory for advanced undergraduate and beginning graduate students, to be followed by a research conference. For more information and resources please visit: https://ctnt-summer.math.uconn.edu/
From playlist CTNT 2020 - Conference Videos

Jacob Lurie: 1/5 Tamagawa numbers in the function field case [2019]
Slides for this talk: http://swc-alpha.math.arizona.edu/video/2019/2019LurieLecture1Slides.pdf Lecture notes: http://swc.math.arizona.edu/aws/2019/2019LurieNotes.pdf Let G be a semisimple algebraic group defined over the field Q of rational numbers and let G(Q) denote the group of ration
From playlist Number Theory

Quadratic forms and homogeneous dynamics by Anish Ghosh
Probabilistic Methods in Negative Curvature ORGANIZERS: Riddhipratim Basu, Anish Ghosh and Mahan Mj DATE: 11 March 2019 to 22 March 2019 VENUE: Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS, Bangalore The focal area of the program lies at the juncture of three areas: Probability theory of random wa
From playlist Probabilistic Methods in Negative Curvature - 2019

What is standard form of a quadratic
👉 Learn the essentials for graphing a quadratic equation. A quadratic equation is an equation of the form y = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b and c are constants. The graph of a quadratic equation is in the shape of a parabola which can either face up or down (if x is squared in the equation) or
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Learn About

John Voight: Computing classical modular forms as orthogonal modular forms
Abstract: Birch gave an extremely efficient algorithm to compute a certain subspace of classical modular forms using the Hecke action on classes of ternary quadratic forms. We extend this method to compute all forms of non-square level using the spinor norm, and we exhibit an implementatio
From playlist Algebraic and Complex Geometry

What is a quadratic equation and its part
👉 Learn the essentials for graphing a quadratic equation. A quadratic equation is an equation of the form y = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b and c are constants. The graph of a quadratic equation is in the shape of a parabola which can either face up or down (if x is squared in the equation) or
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Learn About
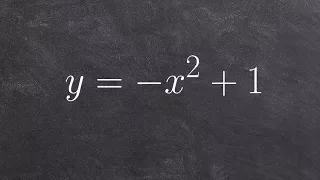
Graphing a quadratic function in standard form
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+c
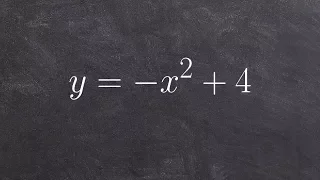
Graphing a quadratic function in standard form
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+c
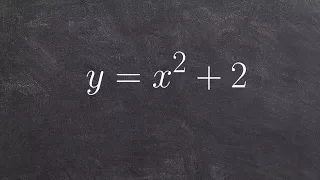
Graphing a quadratic function in standard form
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+c
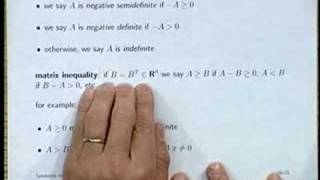
Lecture 16 | Introduction to Linear Dynamical Systems
Professor Stephen Boyd, of the Electrical Engineering department at Stanford University, lectures on the use of symmetric matrices, quadratic forms, matrix norm, and SVDs in LDS for the course Introduction to Linear Dynamical Systems (EE263). Introduction to applied linear algebra and l
From playlist Lecture Collection | Linear Dynamical Systems