
The definition of the characteristic polynomial (without using determinants). The Cayley-Hamilton Theorem.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

How to reorder and classify a polynomial based on it's degree and number of terms
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations
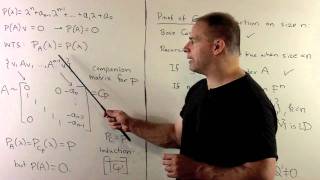
Cayley-Hamilton Theorem: General Case
Matrix Theory: We state and prove the Cayley-Hamilton Theorem over a general field F. That is, we show each square matrix with entries in F satisfies its characteristic polynomial. We consider the special cases of diagonal and companion matrices before giving the proof.
From playlist Matrix Theory

A solution to Weaver's KS2KS2 - Adam Marcus
A solution to Weaver's KS2KS2Primary tabs Adam Marcus Yale University December 2, 2013 We will outline the proof that gives a positive solution of to Weaver's conjecture KS2KS2. That is, we will show that any isotropic collection of vectors whose outer products sum to twice the identity ca
From playlist Mathematics

11/14/2019, Erich Kaltofen, North Carolina State University
Erich Kaltofen, North Carolina State University Title: Proof-of-work Certificates for High Complexity Computations for Linear Algebra Abstract: Computations done by high-power cloud servers such as a Google data center can yield outputs that are easy to verify, such as the factors of an
From playlist Fall 2019 Symbolic-Numeric Computing Seminar

Characteristic subsets and the polynomial method – Miguel Walsh – ICM2018
Dynamical Systems and Ordinary Differential Equations | Number Theory Invited Lecture 9.14 | 3.9 Characteristic subsets and the polynomial method Miguel Walsh Abstract: We provide an informal discussion of the polynomial method. This is a tool of general applicability that can be used to
From playlist Number Theory

Proof of the existence of the minimal polynomial. Every polynomial that annihilates an operator is a polynomial multiple of the minimal polynomial of the operator. The eigenvalues of an operator are precisely the zeros of the minimal polynomial of the operator.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right
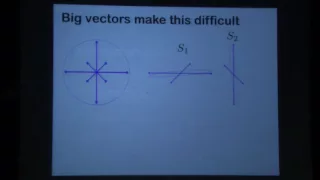
The solution of the Kadison-Singer problem - Daniel Spielman
Daniel Spielman Yale University November 5, 2014 We will explain our recent solution of the Kadison-Singer Problem and the equivalent Bourgain-Tzafriri and Paving Conjectures. We will begin by introducing the method of interlacing families of polynomials and use of barrier function argume
From playlist Mathematics
66 - Multiplicities of eigenvalues
Algebra 1M - international Course no. 104016 Dr. Aviv Censor Technion - International school of engineering
From playlist Algebra 1M

Lecture 30. Fields, field extensions
0:00 Fields 1:48 Examples of fields 08:20 Characteristic of a field 11:20 Prime subfields (Q, F_p) 12:00 Every field has a prime subfield; relation of prime subfield to characteristic 20:15 Frobenius homomorphism 22:40 Field extension 23:50 A field extension of K possesses a structure of
From playlist Abstract Algebra 2
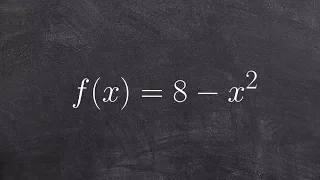
Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations
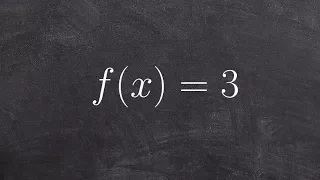
Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations
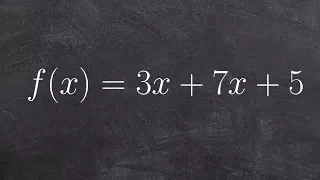
Classify a polynomial and determine degree and leading coefficient
👉 Learn how to classify polynomials. A polynomial is an expression of the sums/differences of two or more terms having different integer exponents of the same variable. A polynomial can be classified in two ways: by the number of terms and by its degree. A monomial is an expression of 1
From playlist Classify Polynomials | Equations

Beyond Eigenspaces: Real Invariant Planes
Linear Algebra: In the context of real vector spaces, one often needs to work with complex eigenvalues. Let A be a real nxn matrix A. We show that, in R^n, there exists at least one of: an (nonzero) eigenvector for A, or a 2-dimensional subspace (plane) invariant under A.
From playlist MathDoctorBob: Linear Algebra I: From Linear Equations to Eigenspaces | CosmoLearning.org Mathematics