Curves | General topology | Topology | Metric geometry
Curve
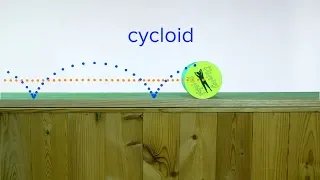
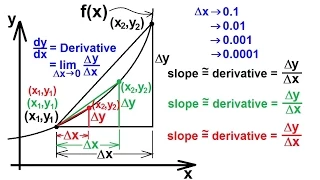
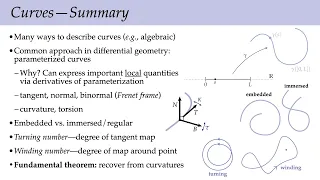
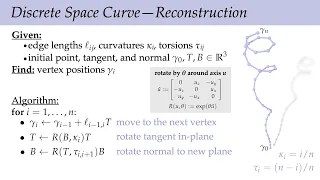
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements: "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: A curve is the image of an interval to a topological space by a continuous function. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a parametrization, and the curve is a parametric curve. In this article, these curves are sometimes called topological curves to distinguish them from more constrained curves such as differentiable curves. This definition encompasses most curves that are studied in mathematics; notable exceptions are level curves (which are unions of curves and isolated points), and algebraic curves (see below). Level curves and algebraic curves are sometimes called implicit curves, since they are generally defined by implicit equations. Nevertheless, the class of topological curves is very broad, and contains some curves that do not look as one may expect for a curve, or even cannot be drawn. This is the case of space-filling curves and fractal curves. For ensuring more regularity, the function that defines a curve is often supposed to be differentiable, and the curve is then said to be a differentiable curve. A plane algebraic curve is the zero set of a polynomial in two indeterminates. More generally, an algebraic curve is the zero set of a finite set of polynomials, which satisfies the further condition of being an algebraic variety of dimension one. If the coefficients of the polynomials belong to a field k, the curve is said to be defined over k. In the common case of a real algebraic curve, where k is the field of real numbers, an algebraic curve is a finite union of topological curves. When complex zeros are considered, one has a complex algebraic curve, which, from the topological point of view, is not a curve, but a surface, and is often called a Riemann surface. Although not being curves in the common sense, algebraic curves defined over other fields have been widely studied. In particular, algebraic curves over a finite field are widely used in modern cryptography. (Wikipedia).