Diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable. (Wikipedia).
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable. (Wikipedia).
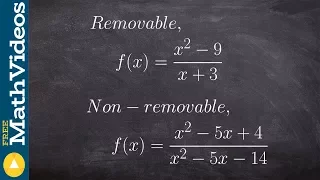
Examples of removable and non removable discontinuities to find limits
👉 Learn how to classify the discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuos if there is a gap in the graph of the function. Some discontinuities are removable while others are non-removable. There is also jump discontinuity. A discontinuity is removable when the denomin
From playlist Holes and Asymptotes of Rational Functions

Determine the discontinuity of the function
👉 Learn how to classify the discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuos if there is a gap in the graph of the function. Some discontinuities are removable while others are non-removable. There is also jump discontinuity. A discontinuity is removable when the denomin
From playlist Holes and Asymptotes of Rational Functions

Find and classify the discontinuity of the rational function
👉 Learn how to classify the discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuos if there is a gap in the graph of the function. Some discontinuities are removable while others are non-removable. There is also jump discontinuity. A discontinuity is removable when the denomin
From playlist Holes and Asymptotes of Rational Functions
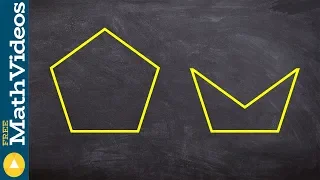
What is the difference between convex and concave polygons
👉 Learn about polygons and how to classify them. A polygon is a plane shape bounded by a finite chain of straight lines. A polygon can be concave or convex and it can also be regular or irregular. A concave polygon is a polygon in which at least one of its interior angles is greater than 1
From playlist Classify Polygons

Homomorphisms in abstract algebra
In this video we add some more definition to our toolbox before we go any further in our study into group theory and abstract algebra. The definition at hand is the homomorphism. A homomorphism is a function that maps the elements for one group to another whilst maintaining their structu
From playlist Abstract algebra

What is the difference between convex and concave
👉 Learn about polygons and how to classify them. A polygon is a plane shape bounded by a finite chain of straight lines. A polygon can be concave or convex and it can also be regular or irregular. A concave polygon is a polygon in which at least one of its interior angles is greater than 1
From playlist Classify Polygons

What is a Manifold? Lesson 12: Fiber Bundles - Formal Description
This is a long lesson, but it is not full of rigorous proofs, it is just a formal definition. Please let me know where the exposition is unclear. I din't quite get through the idea of the structure group of a fiber bundle fully, but I introduced it. The examples in the next lesson will h
From playlist What is a Manifold?

Introduction to Removable and Nonremovable Discontinuities
Introduction to Removable and Nonremovable Discontinuities A complete introduction with definitions, examples, and the intuition behind the definitions.
From playlist Calculus 1 Exam 1 Playlist

Riemannian Exponential Map on the Group of Volume-Preserving Diffeomorphisms - Gerard Misiolek
Gerard Misiolek University of Notre Dame; Institute for Advanced Study October 19, 2011 In 1966 V. Arnold showed how solutions of the Euler equations of hydrodynamics can be viewed as geodesics in the group of volume-preserving diffeomorphisms. This provided a motivation to study the geome
From playlist Mathematics

Metrics on diffeomorphism groups in symplectic and contact geometry - Egor Shelukhin
Short Talks by Postdoctoral Members Egor Shelukhin - September 29, 2015 http://www.math.ias.edu/calendar/event/88294/1443557700/1443558600 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Short Talks by Postdoctoral Members

Matthew D. Foreman: A symbolic representation of Anosov-Katok diffeomorphisms
Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Logic and Foundations
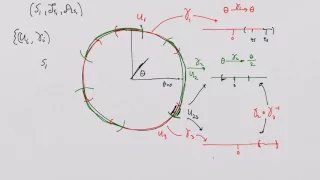
What is a Manifold? Lesson 13: The tangent bundle - an illustration.
What is a Manifold? Lesson 13: The tangent bundle - an illustration. Here we have a close look at a complete example using the tangent bundle of the manifold S_1. Next lesson we look at the Mobius strip as a fiber bundle.
From playlist What is a Manifold?

The general case? - Amie Wilkinson
Members' Seminar Topic: The general case? Speaker: Amie Wilkinson Affiliation: University of Chicago Date: March 25, 2019 For more video please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Riemannian Geometry - Examples, pullback: Oxford Mathematics 4th Year Student Lecture
Riemannian Geometry is the study of curved spaces. It is a powerful tool for taking local information to deduce global results, with applications across diverse areas including topology, group theory, analysis, general relativity and string theory. In these two introductory lectures
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Riemannian Geometry
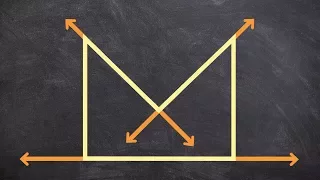
👉 Learn about polygons and how to classify them. A polygon is a plane shape bounded by a finite chain of straight lines. A polygon can be concave or convex and it can also be regular or irregular. A concave polygon is a polygon in which at least one of its interior angles is greater than 1
From playlist Classify Polygons
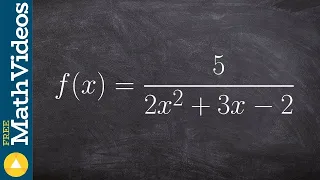
Learn how to find and classify the discontinuity of the function
👉 Learn how to classify the discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuous if there is a gap in the graph of the function. Some discontinuities are removable while others are non-removable. There is also jump discontinuity. A discontinuity is removable when the denomi
From playlist Holes and Asymptotes of Rational Functions

This lecture was held by Abel Laureate John Milnor at The University of Oslo, May 25, 2011 and was part of the Abel Prize Lectures in connection with the Abel Prize Week celebrations. Program for the Abel Lectures 2011 1. "Spheres" by Abel Laureate John Milnor, Institute for Mathematical
From playlist Abel Lectures

The symplectic displacement energy - Peter Spaeth
Peter Spaeth GE Global Research February 20, 2015 To begin we will recall Banyaga's Hofer-like metric on the group of symplectic diffeomorphisms, and explain its conjugation invariance up to a factor. From there we will prove the positivity of the symplectic displacement energy of open su
From playlist Mathematics
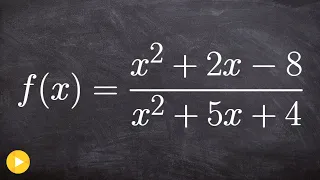
What are removable and non-removable discontinuties
👉 Learn how to find the removable and non-removable discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuous at a point when there is a gap in the graph of the function at that point. A discontinuity is said to be removable when there is a factor in the numerator which can cance
From playlist Find the Asymptotes of Rational Functions

Bruce KLEINER - Ricci flow, diffeomorphism groups, and the Generalized Smale Conjecture
The Smale Conjecture (1961) may be stated in any of the following equivalent forms: • The space of embedded 2-spheres in R3 is contractible. • The inclusion of the orthogonal group O(4) into the group of diffeomorphisms of the 3-sphere is a homotopy equivalence. • The s
From playlist Riemannian Geometry Past, Present and Future: an homage to Marcel Berger