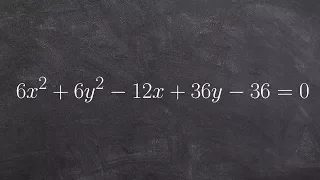Euclidean solid geometry | Birational geometry | Conic sections | Algebraic curves | Analytic geometry
Conic section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a focus, and some particular line, called a directrix, are in a fixed ratio, called the eccentricity. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of degree 2; that is, as the set of points whose coordinates satisfy a quadratic equation in two variables which can be written in the form The geometric properties of the conic can be deduced from its equation. In the Euclidean plane, the three types of conic sections appear quite different, but share many properties. By extending the Euclidean plane to include a line at infinity, obtaining a projective plane, the apparent difference vanishes: the branches of a hyperbola meet in two points at infinity, making it a single closed curve; and the two ends of a parabola meet to make it a closed curve tangent to the line at infinity. Further extension, by expanding the real coordinates to admit complex coordinates, provides the means to see this unification algebraically. (Wikipedia).