Fractions (mathematics) | Elementary mathematics | Rational numbers | Field (mathematics)
Rational number
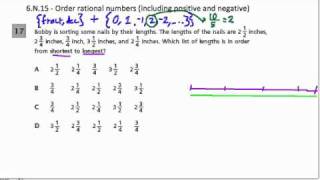
In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. For example, −3/7 is a rational number, as is every integer (e.g. 5 = 5/1). The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface Q, or blackboard bold A rational number is a real number. The real numbers that are rational are those whose decimal expansion either terminates after a finite number of digits (example: 3/4 = 0.75), or eventually begins to repeat the same finite sequence of digits over and over (example: 9/44 = 0.20454545...). This statement is true not only in base 10, but also in every other integer base, such as the binary and hexadecimal ones (see Repeating decimal § Extension to other bases). A real number that is not rational is called irrational. Irrational numbers include √2, π, e, and φ. Since the set of rational numbers is countable, and the set of real numbers is uncountable, almost all real numbers are irrational. Rational numbers can be formally defined as equivalence classes of pairs of integers (p, q) with q ≠ 0, using the equivalence relation defined as follows: The fraction p/q then denotes the equivalence class of (p, q). Rational numbers together with addition and multiplication form a field which contains the integers, and is contained in any field containing the integers. In other words, the field of rational numbers is a prime field, and a field has characteristic zero if and only if it contains the rational numbers as a subfield. Finite extensions of Q are called algebraic number fields, and the algebraic closure of Q is the field of algebraic numbers. In mathematical analysis, the rational numbers form a dense subset of the real numbers. The real numbers can be constructed from the rational numbers by completion, using Cauchy sequences, Dedekind cuts, or infinite decimals (see Construction of the real numbers). (Wikipedia).