Curves | Differential geometry
Differentiable curve
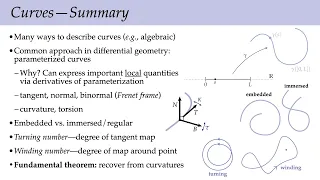
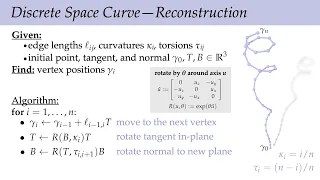
Differential geometry of curves is the branch of geometry that deals with smooth curves in the plane and the Euclidean space by methods of differential and integral calculus. Many specific curves have been thoroughly investigated using the synthetic approach. Differential geometry takes another path: curves are represented in a parametrized form, and their geometric properties and various quantities associated with them, such as the curvature and the arc length, are expressed via derivatives and integrals using vector calculus. One of the most important tools used to analyze a curve is the Frenet frame, a moving frame that provides a coordinate system at each point of the curve that is "best adapted" to the curve near that point. The theory of curves is much simpler and narrower in scope than the theory of surfaces and its higher-dimensional generalizations because a regular curve in a Euclidean space has no intrinsic geometry. Any regular curve may be parametrized by the arc length (the natural parametrization). From the point of view of a theoretical point particle on the curve that does not know anything about the ambient space, all curves would appear the same. Different space curves are only distinguished by how they bend and twist. Quantitatively, this is measured by the differential-geometric invariants called the curvature and the torsion of a curve. The fundamental theorem of curves asserts that the knowledge of these invariants completely determines the curve. (Wikipedia).