Circles | Spherical curves | Elementary geometry | Spherical trigonometry | Riemannian geometry
Great circle
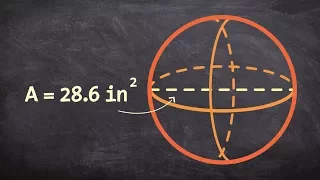
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point. Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geometry are the natural analog of straight lines in Euclidean space. For any pair of distinct non-antipodal points on the sphere, there is a unique great circle passing through both. (Every great circle through any point also passes through its antipodal point, so there are infinitely many great circles through two antipodal points.) The shorter of the two great-circle arcs between two distinct points on the sphere is called the minor arc, and is the shortest surface-path between them. Its arc length is the great-circle distance between the points (the intrinsic distance on a sphere), and is proportional to the measure of the central angle formed by the two points and the center of the sphere. A great circle is the largest circle that can be drawn on any given sphere. Any diameter of any great circle coincides with a diameter of the sphere, and therefore every great circle is concentric with the sphere and shares the same radius. Any other circle of the sphere is called a small circle, and is the intersection of the sphere with a plane not passing through its center. Small circles are the spherical-geometry analog of circles in Euclidean space. Every circle in Euclidean 3-space is a great circle of exactly one sphere. The disk bounded by a great circle is called a great disk: it is the intersection of a ball and a plane passing through its center.In higher dimensions, the great circles on the n-sphere are the intersection of the n-sphere with 2-planes that pass through the origin in the Euclidean space Rn + 1. (Wikipedia).