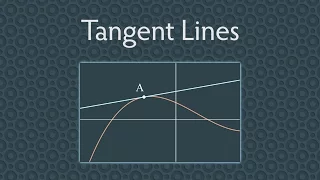
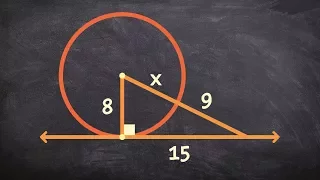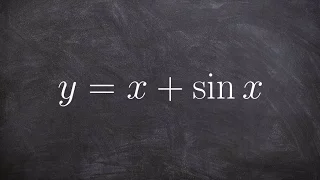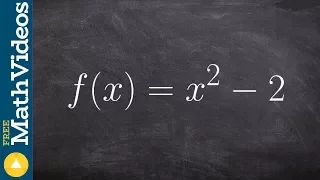Analytic geometry | Differential geometry | Differential topology | Elementary geometry
Tangent
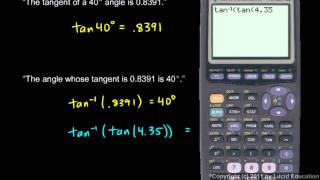
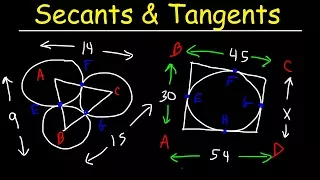
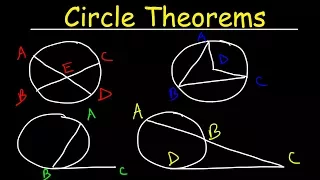
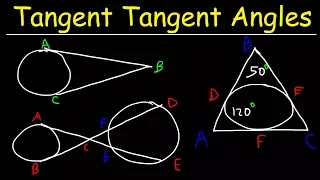
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve y = f(x) at a point x = c if the line passes through the point (c, f(c)) on the curve and has slope f'(c), where f' is the derivative of f. A similar definition applies to space curves and curves in n-dimensional Euclidean space. As it passes through the point where the tangent line and the curve meet, called the point of tangency, the tangent line is "going in the same direction" as the curve, and is thus the best straight-line approximation to the curve at that point. The tangent line to a point on a differentiable curve can also be thought of as a tangent line approximation, the graph of the affine function that best approximates the original function at the given point. Similarly, the tangent plane to a surface at a given point is the plane that "just touches" the surface at that point. The concept of a tangent is one of the most fundamental notions in differential geometry and has been extensively generalized; see Tangent space. The word "tangent" comes from the Latin tangere, "to touch". (Wikipedia).