Analytic geometry | Algebraic curves | Conic sections
Hyperbola
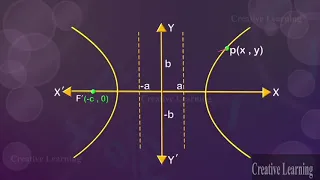
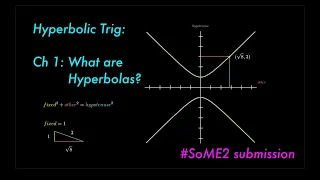
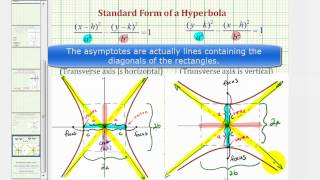
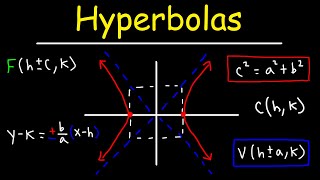
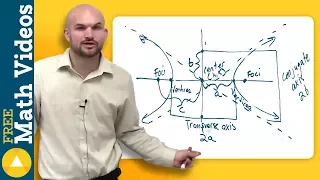
In mathematics, a hyperbola (/haɪˈpɜːrbələ/; pl. hyperbolas or hyperbolae /-liː/; adj. hyperbolic /ˌhaɪpərˈbɒlɪk/) is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola. Hyperbolas arise in many ways: * as the curve representing the reciprocal function in the Cartesian plane, * as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial, * as the shape of an open orbit (as distinct from a closed elliptical orbit), such as the orbit of a spacecraft during a gravity assisted swing-by of a planet or, more generally, any spacecraft (or celestial object) exceeding the escape velocity of the nearest planet or other gravitational body, * as the scattering trajectory of a subatomic particle (acted on by repulsive instead of attractive forces but the principle is the same), * in radio navigation, when the difference between distances to two points, but not the distances themselves, can be determined, and so on. Each branch of the hyperbola has two arms which become straighter (lower curvature) further out from the center of the hyperbola. Diagonally opposite arms, one from each branch, tend in the limit to a common line, called the asymptote of those two arms. So there are two asymptotes, whose intersection is at the center of symmetry of the hyperbola, which can be thought of as the mirror point about which each branch reflects to form the other branch. In the case of the curve the asymptotes are the two coordinate axes. Hyperbolas share many of the ellipses' analytical properties such as eccentricity, focus, and directrix. Typically the correspondence can be made with nothing more than a change of sign in some term. Many other mathematical objects have their origin in the hyperbola, such as hyperbolic paraboloids (saddle surfaces), hyperboloids ("wastebaskets"), hyperbolic geometry (Lobachevsky's celebrated non-Euclidean geometry), hyperbolic functions (sinh, cosh, tanh, etc.), and gyrovector spaces (a geometry proposed for use in both relativity and quantum mechanics which is not Euclidean). (Wikipedia).