Predicate logic | Mathematical notation | Logic symbols
Free variables and bound variables
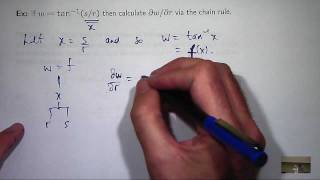
In mathematics, and in other disciplines involving formal languages, including mathematical logic and computer science, a free variable is a notation (symbol) that specifies places in an expression where substitution may take place and is not a parameter of this or any container expression. Some older books use the terms real variable and apparent variable for free variable and bound variable, respectively. The idea is related to a placeholder (a symbol that will later be replaced by some value), or a wildcard character that stands for an unspecified symbol. In computer programming, the term free variable refers to variables used in a function that are neither local variables nor parameters of that function. The term non-local variable is often a synonym in this context. A bound variable, in contrast, is a variable that has been bound to a specific value or range of values in the domain of discourse or universe. This may be achieved through the use of logical quantifiers, variable-binding operators, or an explicit statement of allowed values for the variable (such as, "…where is a positive integer".) Examples are given in the next section. However it is done, the variable ceases to be an independent variable on which the value of the expression depends, whether that value be a truth value or the numerical result of a calculation, or, more generally, an element of an image set of a function. Note that while the domain of discourse in many contexts is understood, when an explicit range of values for the bound variable has not been given, it may be necessary to specify the domain in order to properly evaluate the expression. For example, consider the following expression in which both variables are bound by logical quantifiers: This expression evaluates to false if the domain of and is the real numbers, but true if the domain is the complex numbers. The term "dummy variable" is also sometimes used for a bound variable (more commonly in general mathematics than in computer science), but this should not be confused with the identically named but unrelated concept of dummy variable as used in statistics, most commonly in regression analysis. (Wikipedia).