Distance | Vectors (mathematics and physics) | Euclidean geometry
Distance from a point to a line
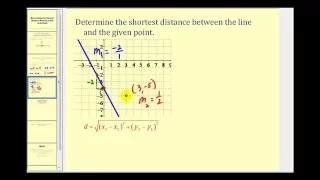
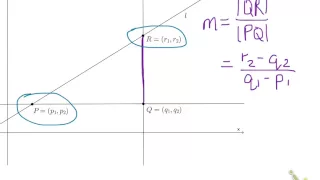
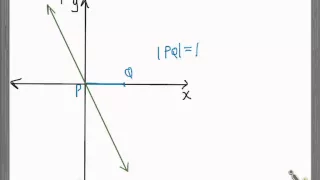
In Euclidean geometry, the 'distance from a point to a line is the shortest distance from a given point to any point on an infinite straight line. It is the perpendicular distance of the point to the line, the length of the line segment which joins the point to nearest point on the line. The formula for calculating it can be derived and expressed in several ways. Knowing the distance from a point to a line can be useful in various situations—for example, finding the shortest distance to reach a road, quantifying the scatter on a graph, etc. In Deming regression, a type of linear curve fitting, if the dependent and independent variables have equal variance this results in orthogonal regression in which the degree of imperfection of the fit is measured for each data point as the perpendicular distance of the point from the regression line. (Wikipedia).