Statistical hypothesis testing
Statistical significance
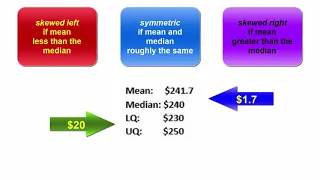
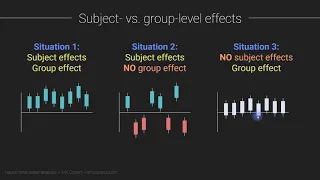
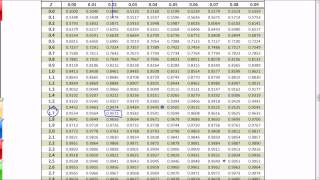
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by , is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the p-value of a result, , is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when . The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the p-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significance level, an investigator may conclude that the effect reflects the characteristics of the whole population, thereby rejecting the null hypothesis. This technique for testing the statistical significance of results was developed in the early 20th century. The term significance does not imply importance here, and the term statistical significance is not the same as research significance, theoretical significance, or practical significance. For example, the term clinical significance refers to the practical importance of a treatment effect. (Wikipedia).