Asymptotic theory (statistics) | Estimator
Consistent estimator
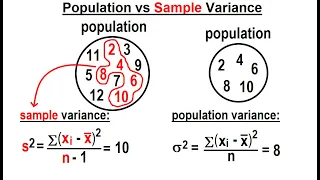
In statistics, a consistent estimator or asymptotically consistent estimator is an estimator—a rule for computing estimates of a parameter θ0—having the property that as the number of data points used increases indefinitely, the resulting sequence of estimates converges in probability to θ0. This means that the distributions of the estimates become more and more concentrated near the true value of the parameter being estimated, so that the probability of the estimator being arbitrarily close to θ0 converges to one. In practice one constructs an estimator as a function of an available sample of size n, and then imagines being able to keep collecting data and expanding the sample ad infinitum. In this way one would obtain a sequence of estimates indexed by n, and consistency is a property of what occurs as the sample size “grows to infinity”. If the sequence of estimates can be mathematically shown to converge in probability to the true value θ0, it is called a consistent estimator; otherwise the estimator is said to be inconsistent. Consistency as defined here is sometimes referred to as weak consistency. When we replace convergence in probability with almost sure convergence, then the estimator is said to be strongly consistent. Consistency is related to bias; see . (Wikipedia).