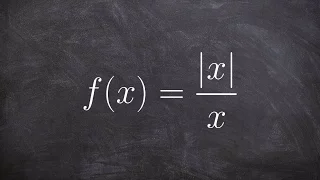Statistical deviation and dispersion | Time series | Errors and residuals | Point estimation performance
Mean absolute error
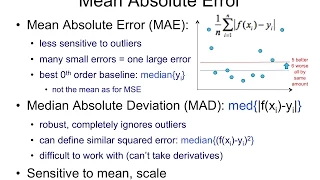
In statistics, mean absolute error (MAE) is a measure of errors between paired observations expressing the same phenomenon. Examples of Y versus X include comparisons of predicted versus observed, subsequent time versus initial time, and one technique of measurement versus an alternative technique of measurement. MAE is calculated as the sum of absolute errors divided by the sample size: It is thus an arithmetic average of the absolute errors , where is the prediction and the true value. Note that alternative formulations may include relative frequencies as weight factors. The mean absolute error uses the same scale as the data being measured. This is known as a scale-dependent accuracy measure and therefore cannot be used to make comparisons between series using different scales. The mean absolute error is a common measure of forecast error in time series analysis, sometimes used in confusion with the more standard definition of mean absolute deviation. The same confusion exists more generally. (Wikipedia).