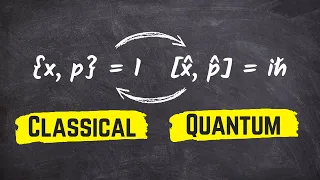Hamiltonian mechanics | Dynamical systems
Hamiltonian mechanics
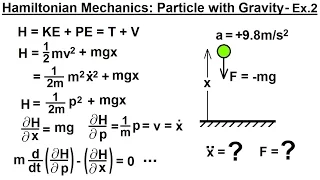
Hamiltonian mechanics emerged in 1833 as a reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics. Introduced by Sir William Rowan Hamilton, Hamiltonian mechanics replaces (generalized) velocities used in Lagrangian mechanics with (generalized) momenta. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena. Hamiltonian mechanics has a close relationship with geometry (notably, symplectic geometry and Poisson structures) and serves as a link between classical and quantum mechanics. (Wikipedia).