Electric charge
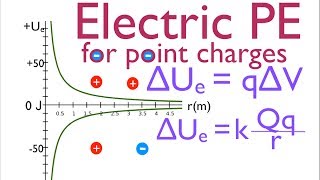
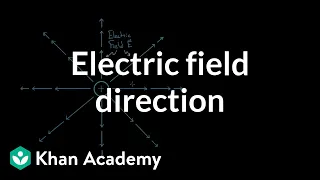
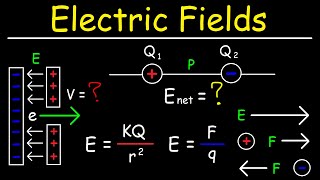
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be positive or negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a negative charge, if there are fewer it will have a positive charge, and if there are equal numbers it will be neutral. Charge is quantized; it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, about 1.602×10−19 C, which is the smallest charge that can exist freely (particles called quarks have smaller charges, multiples of 1/3e, but they are found only in combination, and always combine to form particles that have a charge that is an integer multiple of e). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. Electric charges produce electric fields. A moving charge also produces a magnetic field. The interaction of electric charges with an electromagnetic field (combination of electric and magnetic fields) is the source of the electromagnetic (or Lorentz) force, which is one of the four fundamental forces in physics. The study of photon-mediated interactions among charged particles is called quantum electrodynamics. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. In electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (A⋅h). In physics and chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. Chemistry also uses the Faraday constant, which is the charge on one mole of elementary charges. The lowercase symbol q often denotes charge. (Wikipedia).