Lagrangian mechanics
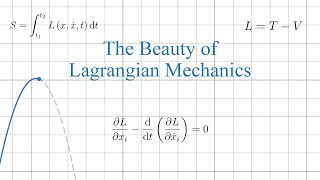
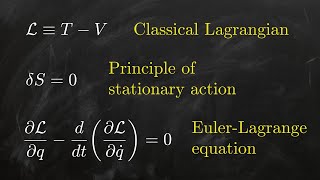
In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the stationary-action principle (also known as the principle of least action). It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his 1788 work, Mécanique analytique. Lagrangian mechanics describes a mechanical system as a pair consisting of a configuration space and a smooth function within that space called a Lagrangian. By convention, where and are the kinetic and potential energy of the system, respectively. The stationary action principle requires that the action functional of the system derived from must remain at a stationary point (a maximum, minimum, or saddle) throughout the time evolution of the system. This constraint allows the calculation of the equations of motion of the system using Lagrange's equations. (Wikipedia).