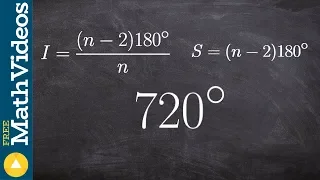Euclidean solid geometry | Angle
Solid angle
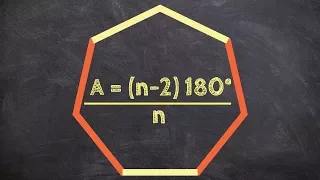
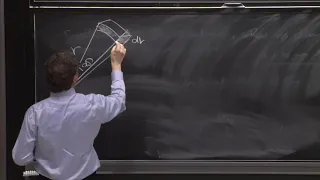
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: Ω) is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point.The point from which the object is viewed is called the apex of the solid angle, and the object is said to subtend its solid angle at that point. In the International System of Units (SI), a solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). One steradian corresponds to one unit of area on the unit sphere surrounding the apex, so an object that blocks all rays from the apex would cover a number of steradians equal to the total surface area of the unit sphere, . Solid angles can also be measured in squares of angular measures such as degrees, minutes, and seconds. A small object nearby may subtend the same solid angle as a larger object farther away. For example, although the Moon is much smaller than the Sun, it is also much closer to Earth. Indeed, as viewed from any point on Earth, both objects have approximately the same solid angle as well as apparent size. This is evident during a solar eclipse. (Wikipedia).