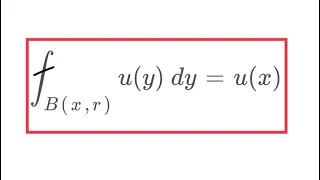Unit sphere
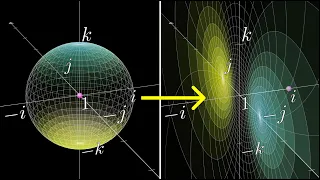
In mathematics, a unit sphere is simply a sphere of radius one around a given center. More generally, it is the set of points of distance 1 from a fixed central point, where different norms can be used as general notions of "distance". A unit ball is the closed set of points of distance less than or equal to 1 from a fixed central point. Usually the center is at the origin of the space, so one speaks of "the unit ball" or "the unit sphere".Special cases are the unit circle and the unit disk. The importance of the unit sphere is that any sphere can be transformed to a unit sphere by a combination of translation and scaling. In this way the properties of spheres in general can be reduced to the study of the unit sphere. (Wikipedia).