Fixed points (mathematics) | Game theory
Fixed point (mathematics)
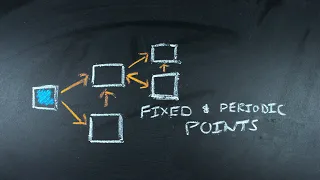
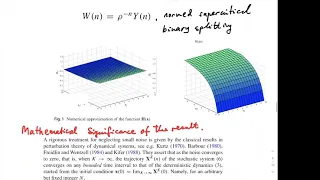
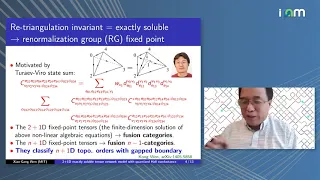
A fixed point (sometimes shortened to fixpoint, also known as an invariant point) is a value that does not change under a given transformation. Specifically, in mathematics, a fixed point of a function is an element that is mapped to itself by the function. In physics, the term fixed point can refer to a temperature that can be used as a reproducible reference point, usually defined by a phase change or triple point. (Wikipedia).