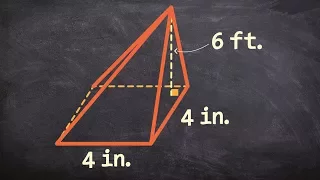Euclidean solid geometry | Quadrics | Surfaces | Algebraic surfaces
Conical surface
In geometry, a (general) conical surface is the unbounded surface formed by the union of all the straight lines that pass through a fixed point — the apex or vertex — and any point of some fixed space curve — the directrix — that does not contain the apex. Each of those lines is called a generatrix of the surface. Every conic surface is ruled and developable. In general, a conical surface consists of two congruent unbounded halves joined by the apex. Each half is called a nappe, and is the union of all the rays that start at the apex and pass through a point of some fixed space curve. (In some cases, however, the two nappes may intersect, or even coincide with the full surface.) Sometimes the term "conical surface" is used to mean just one nappe. If the directrix is a circle , and the apex is located on the circle's axis (the line that contains the center of and is perpendicular to its plane), one obtains the right circular conical surface. This special case is often called a cone, because it is one of the two distinct surfaces that bound the geometric solid of that name. This geometric object can also be described as the set of all points swept by a line that intercepts the axis and rotates around it; or the union of all lines that intersect the axis at a fixed point and at a fixed angle . The aperture of the cone is the angle . More generally, when the directrix is an ellipse, or any conic section, and the apex is an arbitrary point not on the plane of , one obtains an elliptic cone or conical quadric, which is a special case of a quadric surface. A cylindrical surface can be viewed as a limiting case of a conical surface whose apex is moved off to infinity in a particular direction. Indeed, in projective geometry a cylindrical surface is just a special case of a conical surface. (Wikipedia).