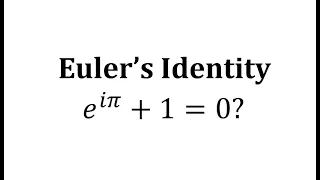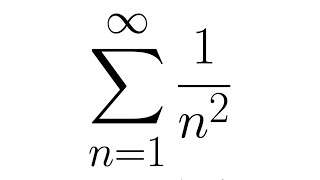Theorems in complex analysis | Articles containing proofs | Trigonometry | E (mathematical constant)
Euler's formula
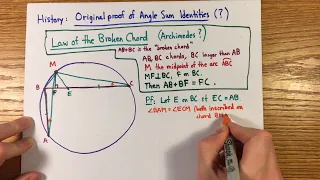
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for any real number x: where e is the base of the natural logarithm, i is the imaginary unit, and cos and sin are the trigonometric functions cosine and sine respectively. This complex exponential function is sometimes denoted cis x ("cosine plus i sine"). The formula is still valid if x is a complex number, and so some authors refer to the more general complex version as Euler's formula. Euler's formula is ubiquitous in mathematics, physics, and engineering. The physicist Richard Feynman called the equation "our jewel" and "the most remarkable formula in mathematics". When x = π, Euler's formula may be rewritten as eiπ + 1 = 0, which is known as Euler's identity. (Wikipedia).