
This is the fourth video of a series from the Worldwide Center of Mathematics explaining the basics of vectors. This video deals with vector magnitude. For more math videos, visit our channel or go to www.centerofmath.org
From playlist Basics: Vectors

Learn how to find the magnitude and direction of the vector
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors

Learn how to find the magnitude and direction of the vector
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors

Learn how to identify the magnitude and direction from a vector given in that form
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors
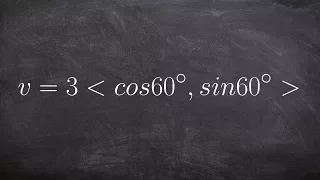
Learn how to identify the magnitude and direction from a vector given in that form
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors

Linear Algebra for Computer Scientists. 2. Magnitude of a Vector
This computer science video is the second in a series about linear algebra for computer scientists. In this video you will learn how to calculate the magnitude of a geometric vector. You will see that to calculate the magnitude of a vector, in two or three dimensions, you must find the
From playlist Linear Algebra for Computer Scientists

Magnitude of the Vector v = (3, -2, 1)
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Magnitude of the Vector v = (3, -2, 1)
From playlist Calculus

Order of Magnitude is a useful tool for estimation, but what are they? In this video I explain what they are and how you can use them. See www.physicshigh.com for all my videos and other resources. If you like this video, please press the LIKE and SHARE with your peers. And please add a CO
From playlist skills and foundations
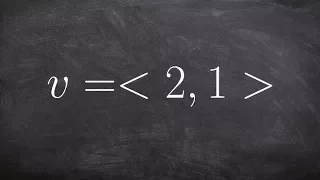
How to determine the angle of a vector as well as use angles to represent vectors
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors

SHM - 16/01/15 - Constructivismes en mathématiques - Frédéric Brechenmacher
Frédéric Brechenmacher (LinX, École polytechnique), « Effectivité et généralité dans la construction des grandeurs algébriques de Kronecker »
From playlist Les constructivismes mathématiques - Séminaire d'Histoire des Mathématiques

Geometry - Scalar Triple Product: Oxford Mathematics 1st Year Student Lecture
To give an insight in to life in Oxford Mathematics we are greatly increasing the number of undergraduate lectures that we are making available. This Geometry lecture from Professor Derek Moulton is taken from his First Year course. This course revisits some ideas encountered in high scho
From playlist Oxford Mathematics 1st Year Student Lectures

1.4: Vector Math II - The Nature of Code
This video continues the discussion about vector mathematics. How to calculate a vector's magnitude (using PVector mag()) and how to normalize a vector (using normalize()) are also discussed. Read along in: http://natureofcode.com/book/chapter-1-vectors/ Contact: https://twitter.com/shi
From playlist The Nature of Code: Simulating Natural Systems

Physics - Advanced E&M: Ch 1 Math Concepts (1 of 55) What is a Unit Vector?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain what is a unit vector and how is express in terms of acceleration, gravity, and E field. Next video in this series can be seen at: https://youtu.be/hiKpoTdFWzg
From playlist PHYSICS 67 ADVANCED ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM

PHYS 125 Lecture 3 (2AB) - Vectors and 2D Kinematics
This lecture discusses vectors: what they are, how to describe them in polar and Cartesian coordinates, and how to switch between those coordinates. Beyond just giving the formulas, advice and strategies on how and when to make these calculations is given. The end of the lecture discuss
From playlist 360 Lecture Capture

Magnitude direction form - vectors - AS level mathematics
How to solve problems related to magnitude direction form. This is a fairly basic skill of converting vectors between magnitude direction form and column vector form or i,j notation. ❤️ ❤️ ❤️ Support the channel ❤️ ❤️ ❤️ https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCf89Gd0FuNUdWv8FlSS7lqQ/joi
From playlist A-level Mathematics Revision

PHYS 125 | Lecture 2B-1 | Vector Math
This lecture is from PHYS 125 at Rice University in the Fall of 2018. It is a 360 video, so be sure to drag the screen to look around!
From playlist PHYS 125 | 2D Kinematics

Lecture 4 - Vectors, part A - Ph1121 Physics - Classical Mechanics
Physics PH 1121 Classical Mechanics - Week 2 Day 1 *** Go Full Screen and make sure you click the gear icon and choose HD. Playlist for classical mechanics course: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL6LNFNTCXeCaDAxx7lxcS4yEK3qFPNvD1 Covered in this Lecture: SCALARS AND VECTORS Displ
From playlist PH1121

Same Math symbol - different meaning
TabletClass Math: https://tcmathacademy.com/ Math help with mathematical symbols and notation. For more math help to include math lessons, practice problems and math tutorials check out my full math help program at https://tcmathacademy.com/ Math Notes: Pre-Algebra Notes: htt
From playlist GED Prep Videos

OCR MEI NEW A Level Maths 2018 Paper 3 Pure Mathematics and Comprehension Walkthrough Q10
Vectors and minimising problem with differentiation! Welcome to my walkthrough of the OCR MEI 2018 NEW SPECIFICATION A Level Maths Paper 3, which is Pure Mathematics and Comprehension (H640/03) Find all of the OCR MEI A Level Maths 2018 paper walkthroughs here: OCR MEI NEW SPECIFICATION
From playlist OCR MEI NEW A Level Maths 2018 Paper 3 Pure Mathematics and Comprehension Walkthrough
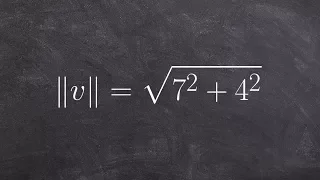
Find the magnitude and direction of a vector
Learn how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector. The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. The magnitude of a vector is obtained by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the components of the vector. The direction of a vector is obtained by taking
From playlist Vectors