Analytic geometry | Circles | Fourier analysis | Trigonometry
Unit circle
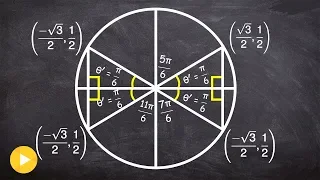
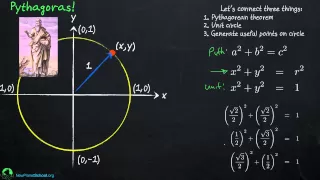
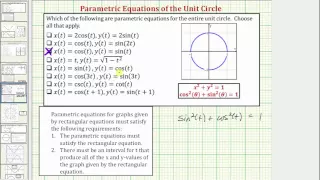
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle of unit radius—that is, a radius of 1. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, the unit circle is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin (0, 0) in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane. In topology, it is often denoted as S1 because it is a one-dimensional unit n-sphere. If (x, y) is a point on the unit circle's circumference, then |x| and |y| are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 1. Thus, by the Pythagorean theorem, x and y satisfy the equation Since x2 = (−x)2 for all x, and since the reflection of any point on the unit circle about the x- or y-axis is also on the unit circle, the above equation holds for all points (x, y) on the unit circle, not only those in the first quadrant. The interior of the unit circle is called the open unit disk, while the interior of the unit circle combined with the unit circle itself is called the closed unit disk. One may also use other notions of "distance" to define other "unit circles", such as the Riemannian circle; see the article on mathematical norms for additional examples. (Wikipedia).