
Kernel of a group homomorphism
In this video I introduce the definition of a kernel of a group homomorphism. It is simply the set of all elements in a group that map to the identity element in a second group under the homomorphism. The video also contain the proofs to show that the kernel is a normal subgroup.
From playlist Abstract algebra

The Kernel of a Group Homomorphism – Abstract Algebra
The kernel of a group homomorphism measures how far off it is from being one-to-one (an injection). Suppose you have a group homomorphism f:G → H. The kernel is the set of all elements in G which map to the identity element in H. It is a subgroup in G and it depends on f. Different ho
From playlist Abstract Algebra
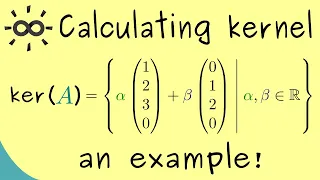
Calculating the kernel of a matrix - An example
Support the channel on Steady: https://steadyhq.com/en/brightsideofmaths Or support me via PayPal: https://paypal.me/brightmaths Here I present some short calculation for the kernel of a matrix. I apologise for my pronunciation. The focus is on the mathematics and not my English skills :)
From playlist Linear algebra (English)
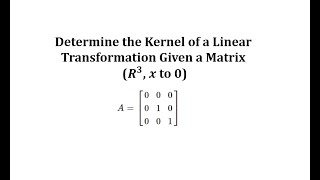
Determine the Kernel of a Linear Transformation Given a Matrix (R3, x to 0)
This video explains how to determine the kernel of a linear transformation.
From playlist Kernel and Image of Linear Transformation

As part of the college algebra series, this Center of Math video will teach you the basics of functions, including how they're written and what they do.
From playlist Basics: College Algebra
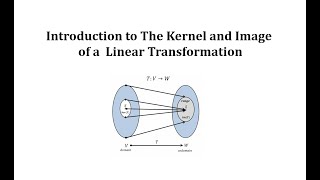
Introduction to the Kernel and Image of a Linear Transformation
This video introduced the topics of kernel and image of a linear transformation.
From playlist Kernel and Image of Linear Transformation
Calculating dimension and basis of range and kernel
German version here: https://youtu.be/lBdwtUa_BGM Support the channel on Steady: https://steadyhq.com/en/brightsideofmaths Official supporters in this month: - Petar Djurkovic - Lukas Mührke Here, I explain the typical calculation scheme for getting dimension and basis for the image/ran
From playlist Linear algebra (English)

Algebra for Beginners | Basics of Algebra
#Algebra is one of the broad parts of mathematics, together with number theory, geometry and analysis. In its most general form, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Table of Conten
From playlist Linear Algebra

Select Which Vectors are in the Kernel of a Matrix (2 by 3)
This video explains how to determine which vectors for a list are in the kernel of a matrix.
From playlist Kernel and Image of Linear Transformation

Richard Gustavson, Manhattan College
April 26, Richard Gustavson, Manhattan College Developing an Algebraic Theory of Integral Equations
From playlist Spring 2022 Online Kolchin seminar in Differential Algebra

Definition of a Subgroup and Proof that the Kernel is a Subgroup
We define what it means for H to be a subgroup of G and give clear criteria which you can follow in order to prove that a given subset is a subgroup. Then we prove that the kernel of f is a subgroup of G. I hope this helps someone learning abstract algebra. Useful Math Supplies https://am
From playlist Group Theory Problems

Jean Michel BISMUT - Fokker-Planck Operators and the Center of the Enveloping Algebra
The heat equation method in index theory gives an explicit local formula for the index of a Dirac operator. Its Lagrangian counterpart involves supersymmetric path integrals. Similar methods can be developed to give a geometric formula for semi simple orbital integrals associated with the
From playlist Integrability, Anomalies and Quantum Field Theory

Volterra integral operators and generalized Reynolds algebras We study algebraic structures underlying Volterra integral operators, in particular the operator identities satisfied by such operators. While the operator satisfies the Rota-Baxter identity when the kernel of the operator only
From playlist DART X

Homological algebra 3: Tor over rings
This lecture is part of an online course on commutative algebra, following the book "Commutative algebra with a view toward algebraic geometry" by David Eisenbud. We define Tor(A,B) for modules A,B over a ring, and comment that it generalizes homology of groups, homology of Lie algebras,
From playlist Commutative algebra

Title: Differential Kernels and Bounds for the Consistency of Differential Equations
From playlist Differential Algebra and Related Topics VII (2016)
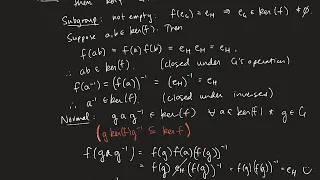
Group Homomorphisms and the big Homomorphism Theorem
This project was created with Explain Everything™ Interactive Whiteboard for iPad.
From playlist Modern Algebra

Ulrich Bauer (3/19/19): Persistence diagrams as diagrams
Title: Persistence Diagrams as Diagrams Abstract: We explore the perspective of viewing persistence diagrams, or persistence barcodes, as diagrams in the categorical sense. Specifically, we consider functors indexed over the reals and taking values in the category of matchings, which has
From playlist AATRN 2019
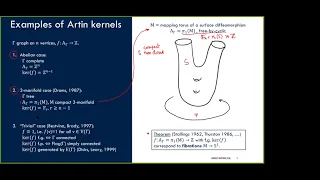
Lorenzo Ruffoni - Graphical splittings of Artin kernels
38th Annual Geometric Topology Workshop (Online), June 15-17, 2021 Lorenzo Ruffoni, Florida State University Title: Graphical splittings of Artin kernels Abstract: A main feature of the theory of right-angled Artin groups (RAAGs) consists in the fact that the algebraic properties of the g
From playlist 38th Annual Geometric Topology Workshop (Online), June 15-17, 2021

Proof that the Kernel of a Linear Transformation is a Subspace
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Proof that the Kernel of a Linear Transformation is a Subspace
From playlist Proofs

Definition of the Kernel of a Group Homomorphism and Sample Proof
Let f be a group homomorphism from G into H. We define the kernel of f as kerf = {x in G | f(x) = e_H} where e_H is the identity in H. Thus is x is in kerf then we have f(x) = e_H. We prove that if the kernel of f contains only the identity element of G, then f must be an injective functio
From playlist Group Theory Problems