
Introduction to Absolute Convergence and Conditional Convergence
Introduction to Absolute Convergence and Conditional Convergence If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. You can also help support my channel by becoming a member https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCr7lmzIk63PZnBw3bezl-Mg/join Thank you:)
From playlist Larson Calculus 9.5 Alternating Series

Infinity Paradox -- Riemann series theorem
Absolute Convergence versus Conditional Convergence
From playlist Physics

Absolute and Conditional Convergence
Learning Objectives: 1) State the definition of Absolute and Conditional Convergence 2) Recognize whether a given series converges absolutely or conditionally 3) Understand the intuition behind the theorem that absolute convergence implies convergence This video is part of a Calculus II c
From playlist Older Calculus II (New Playlist For Spring 2019)

Absolute Convergence, Conditional Convergence, and Divergence
This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into absolute convergence, conditional convergence, and divergence. If the absolute value of the series convergences, then the original series will converge based on the absolute convergence test. If the absolute value of the ser
From playlist New Calculus Video Playlist

Absolute Convergence vs Conditional Convergence vs Convergence
We've seen regular convergence of a series before, but now we consider two special cases. Absolute convergence is when we take the series of the absolute value of the terms, which gets rid of any possible cancellation like what happened a lot in the Alternating Series Test. Absolute conver
From playlist Calculus II (Integration Methods, Series, Parametric/Polar, Vectors) **Full Course**

Interval of Convergence (silent)
Finding the interval of convergence for power series
From playlist 242 spring 2012 exam 3

Find the Interval of Convergence
How to find the interval of convergence for a power series using the root test.
From playlist Convergence (Calculus)

Why is absolute convergence an important concept? - Week 4 - Lecture 3 - Sequences and Series
Subscribe at http://www.youtube.com/kisonecat
From playlist Ohio State: Calculus Two with Jim Fowler: Sequences and Series | CosmoLearning Mathematics

Math 031 040317 Non-nonnegative Series: absolute convergence, Leibniz's test
[Sorry, no sound: the microphone was off.] Convergence test practice - which test would you use? Introduction to arbitrary series (i.e., not necessarily non-negative). Crude tool: absolute convergence implies convergence. Definition of absolute convergence. Conditional convergence. Le
From playlist Course 3: Calculus II (Spring 2017)

Worldwide Calculus: Theorems on Series III: Series with Positive and Negative Terms
Lecture on 'Theorems on Series III: Series with Positive and Negative Terms' from 'Worldwide Integral Calculus' and 'Worldwide AP Calculus'. For more lecture videos and $10 digital textbooks, visit www.centerofmath.org.
From playlist Worldwide Single-Variable Calculus for AP®

Calculus 2, Alternating series (April 13, 2021)
This is a recording of a live class for Math 1172, Calculus 2, an undergraduate course for math majors at Fairfield University, Spring 2021. Class website: http://cstaecker.fairfield.edu/~cstaecker/courses/2021s1172/
From playlist Math 1172 (Calculus 2) Spring 2021
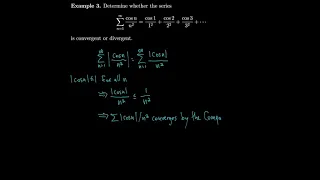
Calculus 11.6 Absolute Convergence, Ratio and Root Tests
My notes are available at http://asherbroberts.com/ (so you can write along with me). Calculus: Early Transcendentals 8th Edition by James Stewart
From playlist Calculus

Calculus BC - Unit 4 Lesson 6: Absolute and Conditional Convergence
AP Calculus BC - Unit 4: Sequences and Series - Lesson 6: Absolute and Conditional Convergence
From playlist AP Calculus BC

Infinite Series Convergence Example using Direct Comparison and Absolute Convergence
Infinite Series Convergence Example using Direct Comparison and Absolute Convergence
From playlist Calculus 2 Exam 4 Playlist

Why do absolutely convergent series just plain converge? - Week 4 - Lecture 2 - Sequences and Series
Subscribe at http://www.youtube.com/kisonecat
From playlist Ohio State: Calculus Two with Jim Fowler: Sequences and Series | CosmoLearning Mathematics

Proof: Limit Law for Quotient of Convergent Sequences | Real Analysis
We prove the limit law for the quotient of convergent sequences. If a_n converges to a and b_n converges to b, then the sequence a_n/b_n converges to a/b, provided that b isn't 0, and each b_n is not 0. Put simply, the quotient of convergent sequences converges to the quotient of their lim
From playlist Real Analysis

Testing for absolute convergence.
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus