Trees (data structures) | Models of computation | Financial models | Mathematical finance
Binomial options pricing model
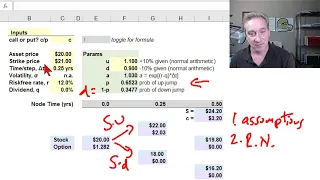
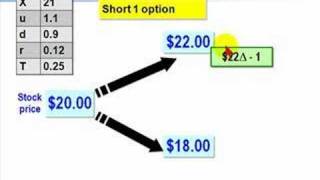
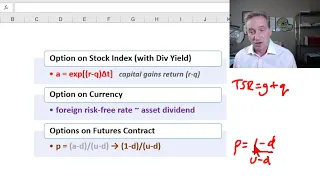
In finance, the binomial options pricing model (BOPM) provides a generalizable numerical method for the valuation of options. Essentially, the model uses a "discrete-time" (lattice based) model of the varying price over time of the underlying financial instrument, addressing cases where the closed-form Black–Scholes formula is wanting. The binomial model was first proposed by William Sharpe in the 1978 edition of Investments (ISBN 013504605X), and formalized by Cox, Ross and Rubinstein in 1979 and by Rendleman and Bartter in that same year. For binomial trees as applied to fixed income and interest rate derivatives see Lattice model (finance) § Interest rate derivatives. (Wikipedia).