Division (mathematics) | Articles containing proofs
Euclidean division
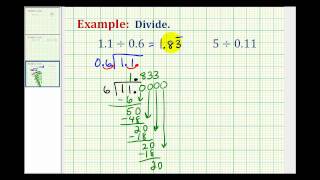
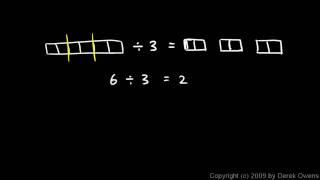
In arithmetic, Euclidean division – or division with remainder – is the process of dividing one integer (the dividend) by another (the divisor), in a way that produces an integer quotient and a natural number remainder strictly smaller than the absolute value of the divisor. A fundamental property is that the quotient and the remainder exist and are unique, under some conditions. Because of this uniqueness, Euclidean division is often considered without referring to any method of computation, and without explicitly computing the quotient and the remainder. The methods of computation are called integer division algorithms, the best known of which being long division. Euclidean division, and algorithms to compute it, are fundamental for many questions concerning integers, such as the Euclidean algorithm for finding the greatest common divisor of two integers, and modular arithmetic, for which only remainders are considered. The operation consisting of computing only the remainder is called the modulo operation, and is used often in both mathematics and computer science. (Wikipedia).