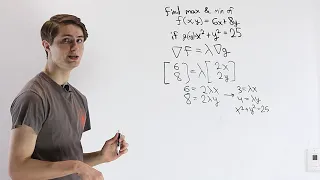Mathematical optimization | Multivariable calculus
Lagrange multiplier
In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints (i.e., subject to the condition that one or more equations have to be satisfied exactly by the chosen values of the variables). It is named after the mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. The basic idea is to convert a constrained problem into a form such that the derivative test of an unconstrained problem can still be applied. The relationship between the gradient of the function and gradients of the constraints rather naturally leads to a reformulation of the original problem, known as the Lagrangian function. The method can be summarized as follows: in order to find the maximum or minimum of a function subjected to the equality constraint , form the Lagrangian function and find the stationary points of considered as a function of and the Lagrange multiplier ; this means that all partial derivatives should be zero, including the partial derivative with respect to . The solution corresponding to the original constrained optimization is always a saddle point of the Lagrangian function, which can be identified among the stationary points from the definiteness of the bordered Hessian matrix. The great advantage of this method is that it allows the optimization to be solved without explicit parameterization in terms of the constraints. As a result, the method of Lagrange multipliers is widely used to solve challenging constrained optimization problems. Further, the method of Lagrange multipliers is generalized by the Karush–Kuhn–Tucker conditions, which can also take into account inequality constraints of the form for a given constant . (Wikipedia).