Euclidean solid geometry | Quadrics | Surfaces | Elementary shapes
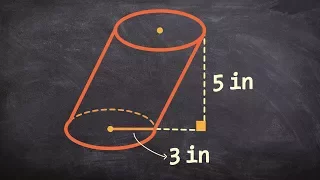
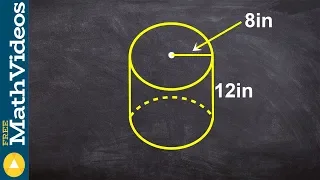
Cylinder
A cylinder (from Greek: κύλινδρος, romanized: kulindros, lit. 'roller', 'tumbler') has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the right circular cylinder. (Wikipedia).