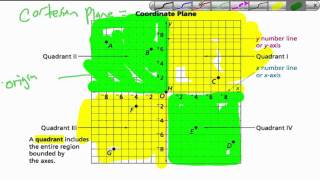
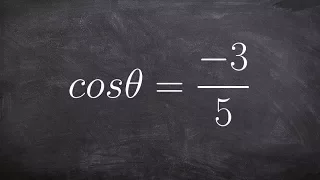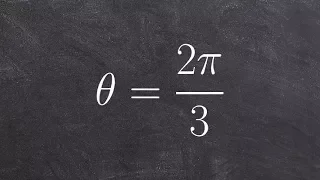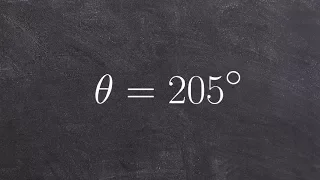Quadrant (plane geometry)
The axes of a two-dimensional Cartesian system divide the plane into four infinite regions, called quadrants, each bounded by two half-axes. These are often numbered from 1st to 4th and denoted by Roman numerals: I (where the signs of the (x; y) coordinates are I (+; +), II (−; +), III (−; −), and IV (+; −). When the axes are drawn according to the mathematical custom, the numbering goes counter-clockwise starting from the upper right ("northeast") quadrant. (Wikipedia).