
(ML 5.1) Exponential families (part 1)
Definition of exponential families, and examples. We look at the Exponential distribution and Bernoulli distribution as examples of exponential families. A playlist of these Machine Learning videos is available here: http://www.youtube.com/view_play_list?p=D0F06AA0D2E8FFBA
From playlist Machine Learning
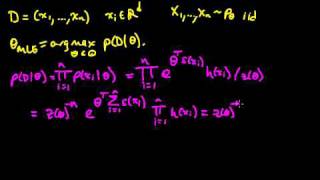
(ML 5.3) MLE for an exponential family (part 1)
Characterization of the MLE for an exponential family. A playlist of these Machine Learning videos is available here: http://www.youtube.com/view_play_list?p=D0F06AA0D2E8FFBA
From playlist Machine Learning
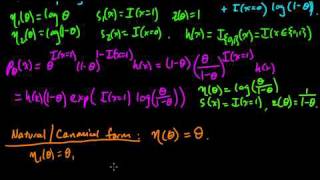
(ML 5.2) Exponential families (part 2)
Definition of exponential families, and examples. We look at the Exponential distribution and Bernoulli distribution as examples of exponential families. A playlist of these Machine Learning videos is available here: http://www.youtube.com/view_play_list?p=D0F06AA0D2E8FFBA
From playlist Machine Learning
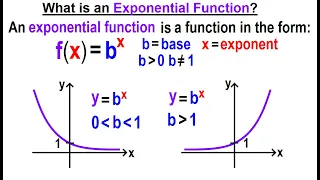
Algebra Ch 46: Exponential Function (1 of 12) What is an Exponential Function?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn an exponential function is a function in the form of f(x)=b^x where b=base (b(greater than)0, and b does not=1) and x=e
From playlist THE "WHAT IS" PLAYLIST

Learn the basics for solve an exponential equation using a calculator
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Learn basics for solving an exponential equation by using one to one property
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms
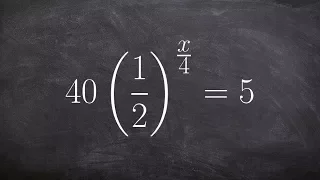
Solving exponential equations using the one to one property
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Stanford CS229: Machine Learning | Summer 2019 | Lecture 6 - Exponential Family & GLM
For more information about Stanford’s Artificial Intelligence professional and graduate programs, visit: https://stanford.io/3Eb7mIi Anand Avati Computer Science, PhD To follow along with the course schedule and syllabus, visit: http://cs229.stanford.edu/syllabus-summer2019.html
From playlist Stanford CS229: Machine Learning Course | Summer 2019 (Anand Avati)

MIT 18.650 Statistics for Applications, Fall 2016 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/18-650F16 Instructor: Philippe Rigollet In this lecture, Prof. Rigollet talked about linear model, generalization, and examples of disease occurring rate, prey capture rate, Kyphosis data, etc.
From playlist MIT 18.650 Statistics for Applications, Fall 2016

Lecture 4 - Perceptron & Generalized Linear Model | Stanford CS229: Machine Learning (Autumn 2018)
For more information about Stanford’s Artificial Intelligence professional and graduate programs, visit: https://stanford.io/3GnSw3o Anand Avati PhD Candidate and CS229 Head TA To follow along with the course schedule and syllabus, visit: http://cs229.stanford.edu/syllabus-autumn2018.h
From playlist Stanford CS229: Machine Learning Full Course taught by Andrew Ng | Autumn 2018

Guido Montúfar : Fisher information metric of the conditional probability politopes
Recording during the thematic meeting : "Geometrical and Topological Structures of Information" the September 01, 2017 at the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent
From playlist Geometry
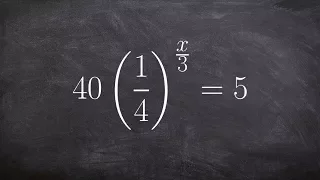
Solve an exponential equation using one to one property and isolating the exponent
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Generalized Linear Model (Part A)
Regression Analysis by Dr. Soumen Maity,Department of Mathematics,IIT Kharagpur.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in
From playlist IIT Kharagpur: Regression Analysis | CosmoLearning.org Mathematics

Solving an exponential equation using the one to one property
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Lecture 4 | Machine Learning (Stanford)
Lecture by Professor Andrew Ng for Machine Learning (CS 229) in the Stanford Computer Science department. Professor Ng lectures on Newton's method, exponential families, and generalized linear models and how they relate to machine learning. This course provides a broad introduction to
From playlist Lecture Collection | Machine Learning

Lecture 11: Sheaves form a topos (Part 2)
In this talk Patrick Elliott proves that the category of sheaves on a site is a topos, by discussing the exponentials and subobject classifier in detail. The notes are already online: The lecture notes are available here: http://therisingsea.org/notes/ch2018-lecture11.pdf. For the genera
From playlist Topos theory seminar

Solving an exponential equation using the one to one property 16^x + 2 = 6
👉 Learn how to solve exponential equations. An exponential equation is an equation in which a variable occurs as an exponent. To solve an exponential equation, we isolate the exponential part of the equation. Then we take the log of both sides. Note that the base of the log should correspo
From playlist Solve Exponential Equations with Logarithms

Generalized Linear Model (Part B)
Regression Analysis by Dr. Soumen Maity,Department of Mathematics,IIT Kharagpur.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in
From playlist IIT Kharagpur: Regression Analysis | CosmoLearning.org Mathematics