Euclidean geometry | Abstract algebra | Linear algebra | Vector calculus | Analytic geometry | Vectors (mathematics and physics)
Euclidean vector
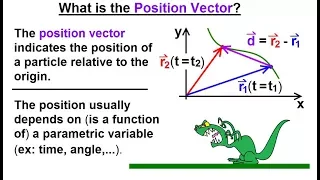
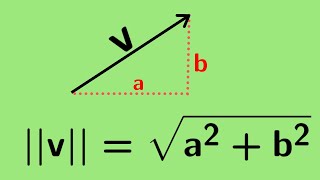
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Vectors can be added to other vectors according to vector algebra. A Euclidean vector is frequently represented by a directed line segment, or graphically as an arrow connecting an initial point A with a terminal point B, and denoted by . A vector is what is needed to "carry" the point A to the point B; the Latin word vector means "carrier". It was first used by 18th century astronomers investigating planetary revolution around the Sun. The magnitude of the vector is the distance between the two points, and the direction refers to the direction of displacement from A to B. Many algebraic operations on real numbers such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and negation have close analogues for vectors, operations which obey the familiar algebraic laws of commutativity, associativity, and distributivity. These operations and associated laws qualify Euclidean vectors as an example of the more generalized concept of vectors defined simply as elements of a vector space. Vectors play an important role in physics: the velocity and acceleration of a moving object and the forces acting on it can all be described with vectors. Many other physical quantities can be usefully thought of as vectors. Although most of them do not represent distances (except, for example, position or displacement), their magnitude and direction can still be represented by the length and direction of an arrow. The mathematical representation of a physical vector depends on the coordinate system used to describe it. Other vector-like objects that describe physical quantities and transform in a similar way under changes of the coordinate system include pseudovectors and tensors. (Wikipedia).