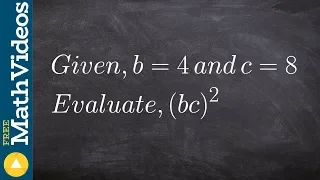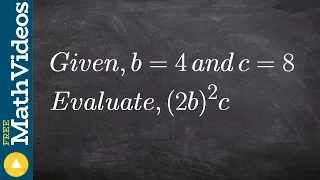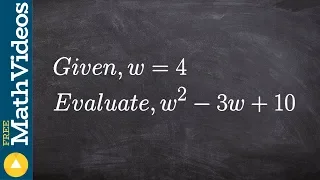Scalar (mathematics)
A scalar is an element of a field which is used to define a vector space.In linear algebra, real numbers or generally elements of a field are called scalars and relate to vectors in an associated vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication (defined in the vector space), in which a vector can be multiplied by a scalar in the defined way to produce another vector. Generally speaking, a vector space may be defined by using any field instead of real numbers (such as complex numbers). Then scalars of that vector space will be elements of the associated field (such as complex numbers). A scalar product operation – not to be confused with scalar multiplication – may be defined on a vector space, allowing two vectors to be multiplied in the defined way to produce a scalar. A vector space equipped with a scalar product is called an inner product space. A quantity described by multiple scalars, such as having both direction and magnitude, is called a vector.The term scalar is also sometimes used informally to mean a vector, matrix, tensor, or other, usually, "compound" value that is actually reduced to a single component. Thus, for example, the product of a 1 × n matrix and an n × 1 matrix, which is formally a 1 × 1 matrix, is often said to be a scalar.The real component of a quaternion is also called its scalar part. The term scalar matrix is used to denote a matrix of the form kI where k is a scalar and I is the identity matrix. (Wikipedia).