Length | Geometric measurement
Displacement (geometry)
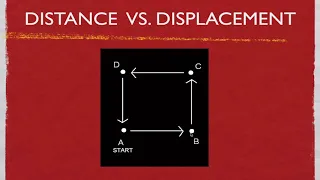
In geometry and mechanics, a displacement is a vector whose length is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P undergoing motion. It quantifies both the distance and direction of the net or total motion along a straight line from the initial position to the final position of the point trajectory. A displacement may be identified with the translation that maps the initial position to the final position. A displacement may be also described as a relative position (resulting from the motion), that is, as the final position xf of a point relative to its initial position xi. The corresponding displacement vector can be defined as the difference between the final and initial positions: In considering motions of objects over time, the instantaneous velocity of the object is the rate of change of the displacement as a function of time. The instantaneous speed, then, is distinct from velocity, or the time rate of change of the distance travelled along a specific path. The velocity may be equivalently defined as the time rate of change of the position vector. If one considers a moving initial position, or equivalently a moving origin (e.g. an initial position or origin which is fixed to a train wagon, which in turn moves on its rail track), the velocity of P (e.g. a point representing the position of a passenger walking on the train) may be referred to as a relative velocity, as opposed to an absolute velocity, which is computed with respect to a point which is considered to be 'fixed in space' (such as, for instance, a point fixed on the floor of the train station). For motion over a given interval of time, the displacement divided by the length of the time interval defines the average velocity, which is a vector, and differs thus from the average speed, which is a scalar quantity. (Wikipedia).