Vector calculus | Vectors (mathematics and physics) | Linear algebra
Pseudovector
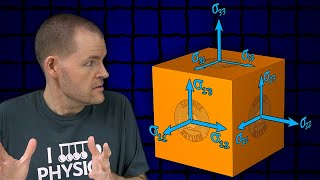
In physics and mathematics, a pseudovector (or axial vector) is a quantity that is defined as a function of some vectors or other geometric shapes, that resembles a vector, and behaves like a vector in many situations, but is changed into its opposite if the orientation of the space is changed, or an improper rigid transformation such as a reflection is applied to the whole figure. Geometrically, the direction of a reflected pseudovector is opposite to its mirror image, but with equal magnitude. In contrast, the reflection of a true (or polar) vector is exactly the same as its mirror image. In three dimensions, the curl of a polar vector field at a point and the cross product of two polar vectors are pseudovectors. One example of a pseudovector is the normal to an oriented plane. An oriented plane can be defined by two non-parallel vectors, a and b, that span the plane. The vector a × b is a normal to the plane (there are two normals, one on each side – the right-hand rule will determine which), and is a pseudovector. This has consequences in computer graphics where it has to be considered when transforming surface normals. A number of quantities in physics behave as pseudovectors rather than polar vectors, including magnetic field and angular velocity. In mathematics, in three-dimensions, pseudovectors are equivalent to bivectors, from which the transformation rules of pseudovectors can be derived. More generally in n-dimensional geometric algebra pseudovectors are the elements of the algebra with dimension n − 1, written ⋀n−1 Rn. The label "pseudo" can be further generalized to pseudoscalars and pseudotensors, both of which gain an extra sign flip under improper rotations compared to a true scalar or tensor. (Wikipedia).