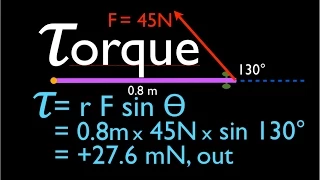
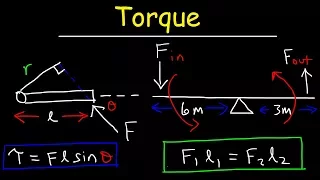
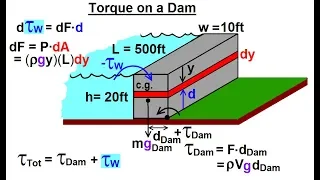
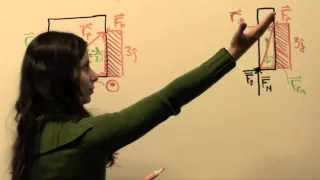Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment, moment of force, rotational force or turning effect, depending on the field of study. It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the force and the perpendicular distance of the line of action of a force from the axis of rotation. The law of Conservation of energy can also be used to understand Torque. The symbol for torque is typically , the lowercase Greek letter tau. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by M. In three dimensions, the torque is a pseudovector; for point particles, it is given by the cross product of the position vector (distance vector) and the force vector. The magnitude of torque of a rigid body depends on three quantities: the force applied, the lever arm vector connecting the point about which the torque is being measured to the point of force application, and the angle between the force and lever arm vectors. In symbols: where * is the torque vector and is the magnitude of the torque, * is the position vector (a vector from the point about which the torque is being measured to the point where the force is applied), * is the force vector, * denotes the cross product, which produces a vector that is perpendicular to both r and F following the right-hand rule, * is the angle between the force vector and the lever arm vector. The SI unit for torque is the newton-metre (N⋅m). For more on the units of torque, see . (Wikipedia).