
k-NN 4: which distance function?
[http://bit.ly/k-NN] The nearest-neighbour algorithm is sensitive to the choice of distance function. Euclidean distance (L2) is a common choice, but it may lead to sub-optimal performance. We discuss Minkowski (p-norm) distance functions, which generalise the Euclidean distance, and can a
From playlist Nearest Neighbour Methods

The distance formula in multidimensional spaces... and vectors too -- Calculus III
This lecture is on Calculus III. It follows Part III of the book Calculus Illustrated by Peter Saveliev. The text of the book can be found at http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Calculus III

Euclidean and non-Euclidean metrics -- Proofs
This lecture is on Introduction to Higher Mathematics (Proofs). For more see http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Proofs
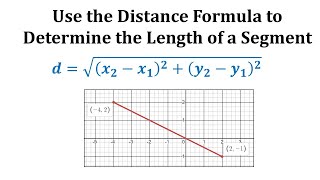
Example: Determine the Distance Between Two Points
This video shows an example of determining the length of a segment on the coordinate plane by using the distance formula. Complete Video List: http://www.mathispower4u.yolasite.com or http://www.mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Using the Distance Formula / Midpoint Formula
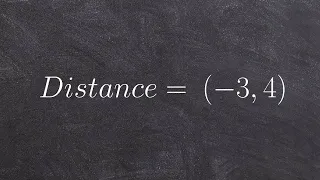
Determine the distance between two points on a coordinate axis
👉 Learn how to find the distance between two points. The distance between two points is the length of the line joining the two points in the coordinate plane. To find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane, we make use of the formula d = sqrt((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2). 👏
From playlist Find the Distance of the Line Segment

Distance between Two Points in Space (-3, 2, 5) and (4, 0, 8)
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Distance between Two Points in Space (-3, 2, 5) and (4, 0, 8)
From playlist Calculus

Multidimensional Scaling - An EXTREMELY POWERFUL algorithm
Entry to #some2 Multidimensional scaling is also similar to PCA and has other names as well. I hope this video informs you of the basics. You can probably analyse a clean dataset using it now if you know some R or Python. Top 1000 Instagram Influencer dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/d
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition 2 videos
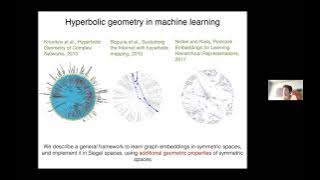
Anna Wienhard (7/29/22): Graph Embeddings in Symmetric Spaces
Abstract: Learning faithful graph representations has become a fundamental intermediary step in a wide range of machine learning applications. We propose the systematic use of symmetric spaces as embedding targets. We use Finsler metrics integrated in a Riemannian optimization scheme, that
From playlist Applied Geometry for Data Sciences 2022

Data Science for Uncertainty Quantification
Chapter 3 of the book, covers mostly dimension reduction
From playlist Uncertainty Quantification
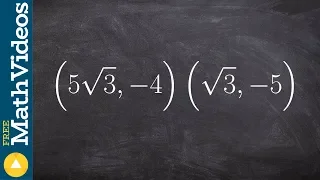
Find the distance between the two coordinate points ex 1
👉 Learn how to find the distance between two points. The distance between two points is the length of the line joining the two points in the coordinate plane. To find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane, we make use of the formula d = sqrt((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2). 👏
From playlist Find the Distance of the Line Segment

IGA: Rigidity of Riemannian embeddings of discrete metric spaces - Matan Eilat
Abstract: Let M be a complete, connected Riemannian surface and suppose that S is a discrete subset of M. What can we learn about M from the knowledge of all distances in the surface between pairs of points of S? We prove that if the distances in S correspond to the distances in a 2-dimens
From playlist Informal Geometric Analysis Seminar
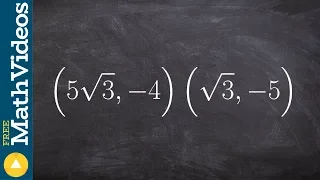
Find the distance between two coordinate points ex1
👉 Learn how to find the distance between two points. The distance between two points is the length of the line joining the two points in the coordinate plane. To find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane, we make use of the formula d = sqrt((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2). 👏
From playlist Find the Distance of the Line Segment

Concentration of Measure on the Compact Classical Matrix Groups - Elizabeth Meckes
Elizabeth Meckes Case Western Reserve Univ May 20, 2014 For more videos, visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Linear Algebra 6.1 Inner Products
My notes are available at http://asherbroberts.com/ (so you can write along with me). Elementary Linear Algebra: Applications Version 12th Edition by Howard Anton, Chris Rorres, and Anton Kaul A. Roberts is supported in part by the grants NSF CAREER 1653602 and NSF DMS 2153803.
From playlist Linear Algebra

An Intuitive Introduction to Projective Geometry Using Linear Algebra
This is an area of math that I've wanted to talk about for a long time, especially since I have found how projective geometry can be used to formulate Euclidean, spherical, and hyperbolic geometries, and a possible (and hopefully plausible) way projective geometry (specifically the model t
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition 2 videos

Metric and manifold repair for missing data - Anna Gilbert
Virtual Workshop on Missing Data Challenges in Computation Statistics and Applications Topic: Metric and manifold repair for missing data Speaker: Anna Gilbert Date: September 11, 2020 For more video please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics
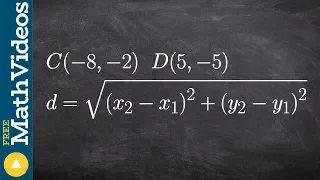
Using the distance formula to determine the distance between two coordinate points
👉 Learn how to find the distance between two points. The distance between two points is the length of the line joining the two points in the coordinate plane. To find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane, we make use of the formula d = sqrt((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2). 👏
From playlist Find the Distance of the Line Segment

T. Richard - Advanced basics of Riemannian geometry 2
We will present some of the tools used by the more advanced lectures. The topics discussed will include : Gromov Hausdorff distance, comparison theorems for sectional and Ricci curvature, the Bochner formula and basics of Ricci flow.
From playlist Ecole d'été 2021 - Curvature Constraints and Spaces of Metrics

