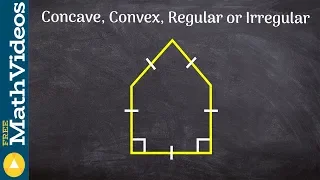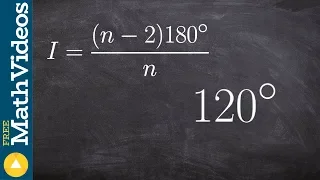Regular polygon
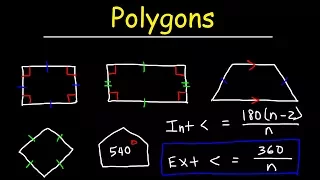
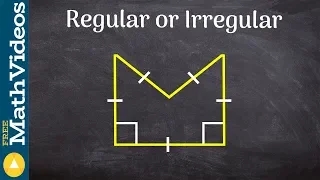
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex, star or skew. In the limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a straight line), if the edge length is fixed. (Wikipedia).