
Applied Portfolio Management - Video 4 - Fixed Income Asset Management
All slides are available on my Patreon page: https://www.patreon.com/PatrickBoyleOnFinance Fixed income refers to any type of investment under which the borrower or issuer is obliged to make payments of a fixed amount on a fixed schedule. For example, the borrower may have to pay interest
From playlist Applied Portfolio Management

What is a Protective Put? Options Trading Strategies
These classes are all based on the book Trading and Pricing Financial Derivatives, available on Amazon at this link. https://amzn.to/2WIoAL0 Check out our website http://www.onfinance.org/ Follow Patrick on twitter here: https://twitter.com/PatrickEBoyle What is a Protective Put? A pr
From playlist Class 2: An Introduction to Options

Financial Options Pricing History. How do Investors Price Options?
Financial Options Pricing History. Today we will learn How do Investors Price Options? These classes are all based on the book Trading and Pricing Financial Derivatives, available on Amazon at this link. https://amzn.to/2WIoAL0 Check out our website http://www.onfinance.org/ Follow Patri
From playlist Class 2: An Introduction to Options

How To Calculate Your Average Cost Basis When Investing In Stocks
This video tutorial explains how to calculate the average cost basis or average cost per share when making multiple investment purchases of the same stock at different prices. Stock Trading Strategies For Beginners: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7IBzTZqeyo0 Call and Put Options: https:
From playlist Stocks and Bonds
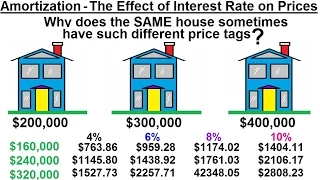
Business Math - Finance Math (22 of 30) Amortization - The Effect of Interest Rates on Prices
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain the effect of interest rate on the price of purchasing a home. Next video in this series can be seen at: http://youtu.be/moEZfOVpEog
From playlist BUSINESS MATH 2 FINANCE MATH

What is an Options Contract in Finance
These classes are all based on the book Trading and Pricing Financial Derivatives, available on Amazon at this link. https://amzn.to/2WIoAL0 Check out our website http://www.onfinance.org/ Follow Patrick on twitter here: https://twitter.com/PatrickEBoyle What are Financial Options? Opt
From playlist Class 2: An Introduction to Options

10. Debt Markets: Term Structure
Financial Markets (ECON 252) The markets for debt, both public and private far exceed the entire stock market in value and importance. The U.S. Treasury issues debt of various maturities through auctions, which are open only to authorized buyers. Corporations issue debt with investment
From playlist Financial Markets (2008) with Robert Shiller

Financial Futures Payoff Diagrams
Financial Futures Payoff Diagrams In This Video we look at the payoff diagrams of being long and short futures contracts and how this might differ from being long and short the underlying. We learn a bit about how an investor shorts a given underlying and why it might be more efficient to
From playlist Class 1 Futures & Forwards

Instead of a fixed strike price, an exchange option gives the holder the right to purchase an asset (denoted V in screencast) with another asset (denoted U). Examples include exchange one currency for another; Executive stock options indexed to S&P500. For more financial risk videos, visit
From playlist Derivatives: Exotic Options
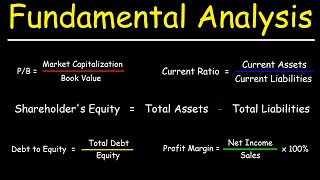
This video explains how to use fundamental analysis to determine if a company may be undervalued or overvalued by using valuation ratios such as the price to book ratio, price to sales, & price to earnings ratio. It also explains how to determine if a company may go bankrupt using the deb
From playlist Stocks and Bonds

Introduction to Derivatives - Futures & Forwards - Revision Class1
A revision slideshow on Futures and Forwards. These classes are all based on the book Trading and Pricing Financial Derivatives, available on Amazon at this link. https://amzn.to/2WIoAL0 Check out our website http://www.onfinance.org/ Follow Patrick on twitter here: https://twitter.com
From playlist Revision Lectures

Exotic option: exchange option (FRM T3-47)
[my xls is here https://trtl.bz/2C9PEXC] Instead of a fixed exercise price, an exchange option has an exercise price linked to some other asset. In my illustrated example here, the exchange option holder will pay (as the exercise price) 80X the price of silver in exchange for receiving one
From playlist FM&P: Intro to Derivatives: Exotic options (FRM Topic 3)

Risk Management Lesson 2A: CAPM and the Greeks
First part of the second lesson. Topics: - Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) - Quick review of markets and financial products - The Greeks (first part)
From playlist Risk Management

QRM 10-1: The Greeks for Market Risk
Lesson 10 is devoted to the model building approach to market risk. To use such an approach, we need some basic tools from financial mathematics and basic risk management, an example being the Greeks and duration (which nevertheless is linked to the Greeks). For those of you who are not fa
From playlist Quantitative Risk Management

BEM1105x Course Playlist - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL8_xPU5epJdfCxbRzxuchTfgOH1I2Ibht Produced in association with Caltech Academic Media Technologies. ©2020 California Institute of Technology
From playlist BEM1105x Course - Prof. Jakša Cvitanić

Types of Assets: Financial, Tangible, and Intangible
How do people get rich? Rather than having very high-paying jobs, wealth is more easily accumulated through ownership of assets. This is anything of value that can be converted into money. Of course we know about assets like houses and other properties, or even expensive collectibles, but
From playlist Economics

Enterprise value | Stocks and bonds | Finance & Capital Markets | Khan Academy
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/core-finance/stock-and-bonds/valuation-and-investing/v/enterprise-value Solving the P/E conundrum by looking at a different valuation metric (e
From playlist Stocks and bonds | Finance and Capital Markets | Khan Academy


