
Solving an equation by combining like terms 6=5c–9–2c
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with Two Variables
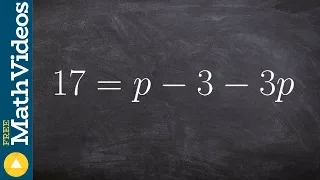
Solving and equation with the variable on the same side ex 3, 17=p–3–3p
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with Two Variables
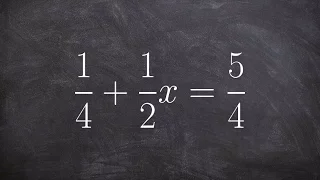
Solving a linear equation with fractions in two different ways two step equation
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with Fractions
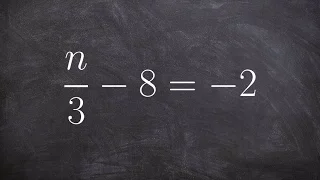
Learn to solve a two step equation with a number in the denominator
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Fraction

Linear and quadratic approximations -- Calculus II
This lecture is on Calculus II. It follows Part II of the book Calculus Illustrated by Peter Saveliev. The text of the book can be found at http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Calculus II

Why Algebraic Data Types Are Important
Strong static typing detects a lot of bugs at compile time, so why would anyone prefer to program in JavaScript or Python? The main reason is that type systems can be extremely complex, often with byzantine typing rules (C++ comes to mind). This makes generic programming a truly dark art.
From playlist Functional Programming

Kurusch EBRAHIMI-FARD - Wick Products and Combinatorial Hopf Algebras
Wick products play a central role in both quantum field theory and stochastic calculus. They originated in Wick’s work from 1950. In this talk we will describe Wick products using combinatorial Hopf algebra. Based on joint work with F. Patras, N. Tapia, L. Zambotti. https://indico.math.c
From playlist Algebraic Structures in Perturbative Quantum Field Theory: a conference in honour of Dirk Kreimer's 60th birthday

The Monomial Structure of Boolean Functions - Shachar Lovett
Workshop on Additive Combinatorics and Algebraic Connections Topic: The Monomial Structure of Boolean Functions Speaker: Shachar Lovett Affiliation: University of California, San Diego Date: October 25, 2022 Let f:0,1n to 0,1 be a boolean function. It can be uniquely represented as a mu
From playlist Mathematics

Lilya Budaghyan : On APN and AB power functions
CONFERENCE Recording during the thematic meeting : « ALgebraic and combinatorial methods for COding and CRYPTography» the February 23, 2023 at the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given b
From playlist Combinatorics

Solving an equation with two terms in the numerator
👉 Learn how to solve two step rational linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. A rational equation is an equation containing at least one fraction whose numerator and (or) denominator are polynomials. To solve for a variable in a
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Rational Fraction

Solving an equation with two terms in the numerator
👉 Learn how to solve two step rational linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. A rational equation is an equation containing at least one fraction whose numerator and (or) denominator are polynomials. To solve for a variable in a
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Rational Fraction
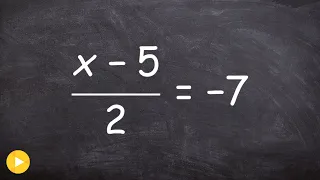
Solving an equation with two terms in the numerator
👉 Learn how to solve two step rational linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. A rational equation is an equation containing at least one fraction whose numerator and (or) denominator are polynomials. To solve for a variable in a
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Rational Fraction
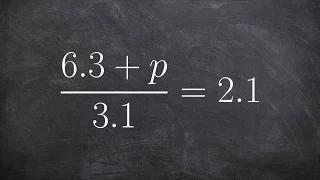
Solving an equation with two terms in the numerator
👉 Learn how to solve two step rational linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. A rational equation is an equation containing at least one fraction whose numerator and (or) denominator are polynomials. To solve for a variable in a
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Rational Fraction

Gilles de Castro: C*-algebras and Leavitt path algebras for labelled graphs
Talk by Gilles de Castro at Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Americas) on November 19, 2021. https://globalncgseminar.org/talks/tba-16/
From playlist Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Americas)

Squashing theories into Heyting algebras
This is the first of two videos on Heyting algebra, Tarski-Lindenbaum and negation: https://gist.github.com/Nikolaj-K/1478e66ccc9b7ac2ea565e743c904555 Followup video: https://youtu.be/ws6vCT7ExTY
From playlist Logic

Chi-Keung Ng: Ortho-sets and Gelfand spectra
Talk by Chi-Keung Ng in Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Europe) http://www.noncommutativegeometry.nl/ncgseminar/ on June 9, 2021
From playlist Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Europe)

Model Theory - part 04 - Posets, Lattices, Heyting Algebras, Booleans Algebras
This is a short video for people who haven't seen a Heyting algebras before. There is really nothing special in it that doesn't show up in wikipedia or ncatlab. I just wanted to review it before we use them. Errata: *at 3:35: there the law should read (a and (a or b) ), not (a and (a and
From playlist Model Theory

Camille Male - Distributional symmetry of random matrices...
Camille Male - Distributional symmetry of random matrices and the non commutative notions of independence
From playlist Spectral properties of large random objects - Summer school 2017

This is a follow up to https://youtu.be/lDhKE2SKF08. In this video we zoom in on Negation and also discuss models such as the 3-valued one for intuitionistic propositional logic. The script I'm using you can find here: https://gist.github.com/Nikolaj-K/1478e66ccc9b7ac2ea565e743c904555
From playlist Logic
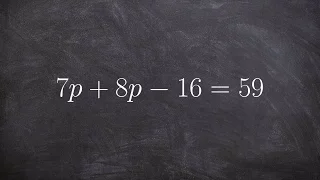
Solving an equation with variable on the same side
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with Two Variables