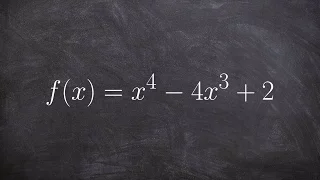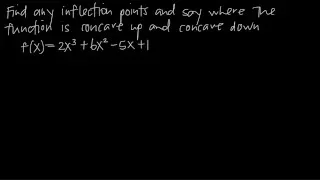Convex analysis | Types of functions
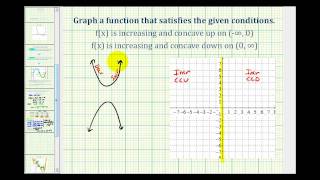
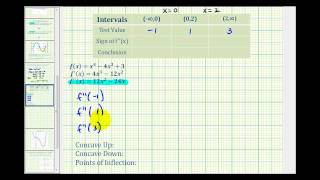
Concave function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex. (Wikipedia).