
What is a Sampling Distribution?
Intro to sampling distributions. What is a sampling distribution? What is the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean? Check out my e-book, Sampling in Statistics, which covers everything you need to know to find samples with more than 20 different techniques: https://prof-essa.creat
From playlist Probability Distributions

Sampling Distribution of the PROPORTION: Friends of P (12-2)
The sampling distribution of the proportion is the probability distribution of all possible values of the sample proportions. It is analogous to the Distribution of Sample Means. When the sample size is large enough, the sampling distribution of the proportion can be approximated by a norm
From playlist Sampling Distributions in Statistics (WK 12 - QBA 237)

Sampling Distributions of Means
This is an old video. See StatsMrR.com for access to hundreds of 1-3 minute, well-produced videos for learning Statistics. In this older video: Understanding and working with sampling distributions of means. Calculating the mean and standard deviation and the probability associated with
From playlist Older Statistics Videos and Other Math Videos

Conditions Required to Use Normal to Approximate Sample Proportions
Sample proportions, like binomial successes, are discrete. As long as large samples are taken so np and n(1-p) are both at least 10, a continuous normal distribution yields an acceptable approximation of the probabilities associated with a sample proportion distribution.
From playlist Unit 7 Probability C: Sampling Distributions & Simulation
The Normal Distribution (1 of 3: Introductory definition)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist The Normal Distribution

How to Choose a SAMPLING Method (12-7)
When possible, use probability sampling methods, such as simple random, stratified, cluster, or systematic sampling.
From playlist Sampling Distributions in Statistics (WK 12 - QBA 237)
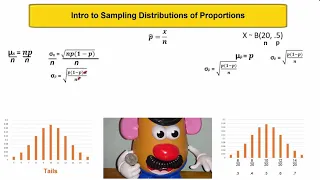
An overview and introduction to understanding sampling distributions of proportions [sample proportions] and how to calculate them
From playlist Unit 7 Probability C: Sampling Distributions & Simulation

An overview of the most popular sampling methods used in statistics. Check out my e-book, Sampling in Statistics, which covers everything you need to know to find samples with more than 20 different techniques: https://prof-essa.creator-spring.com/listing/sampling-in-statistics
From playlist Sampling

Statistics - Types of sampling
This video will show you the many ways that you could sample. Remember to look for those small differences such as if you are breaking things into groups first. For more videos visit http://www.mysecretmathtutor.com
From playlist Statistics

Central Limit Theorem - Sampling Distribution of Sample Means - Stats & Probability
This statistics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the central limit theorem. It explains that a sampling distribution of sample means will form the shape of a normal distribution regardless of the shape of the population distribution if a large enough sample is taken from
From playlist Statistics

0:15 - Review 2:29 - Learning objectives 2:48 - 1. Construct and interpret sampling distributions using StatKey 3:36 - StatKey 10:42 - Review of terms 12:12 - 2. Explain the general form of a confidence interval 16:59 - 3. Interpret a confidence interval 23:47 - 4. Explain the
From playlist STAT 200 Video Lectures

Lec 6 | MIT 2.830J Control of Manufacturing Processes, S08
Lecture 6: Sampling distributions and statistical hypotheses Instructor: Duane Boning, David Hardt View the complete course at: http://ocw.mit.edu/2-830JS08 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 2.830J, Control of Manufacturing Processes S08

Central Limit Theorem and the Distribution of Sample Means in Business Statistics (Week 11D)
Description Using our new sampling techniques, we now have dozens of samples from our population, but how can we use them to estimate the population mean? We can create a sampling distribution of the means from each sample, and with the central limit theorem, we learn something remarkable:
From playlist Basic Business Statistics (QBA 237 - Missouri State University)

05-5 Inverse modeling : sequential importance re-sampling
Introduction to sequential importance resampling
From playlist QUSS GS 260

Brief Introduction to Probability and Simulation: Part 3 - Elaine Spiller
PROGRAM: Data Assimilation Research Program Venue: Centre for Applicable Mathematics-TIFR and Indian Institute of Science Dates: 04 - 23 July, 2011 DESCRIPTION: Data assimilation (DA) is a powerful and versatile method for combining observational data of a system with its dynamical mod
From playlist Data Assimilation Research Program

The Central Limit Theorem – With Examples in Python
In today's video, I empirically demonstrate the central limit theorem using Python, and briefly cover its importance to data science. Hand-On example available as a GitHub Gist at: http://bit.ly/JKcentral Dr. Jon Krohn is Chief Data Scientist at untapt, and the #1 Bestselling author of De
From playlist Talks and Tutorials

From playlist STAT 200 Video Lectures
Excel Statistical Analysis 37: Learn Central Limit Theorem by Building Sampling Distribution of Xbar
Download Excel File: https://excelisfun.net/files/Ch07-ESA.xlsm PDF notes file: https://excelisfun.net/files/Ch07-ESA.pdf Learn about one of the most power rules in statistics: the Central Limit Theorem by building a Sampling Distribution of Sample Means (Xbar). Learn how to calculate the
From playlist Excel Statistical Analysis for Business Class Playlist of Videos from excelisfun
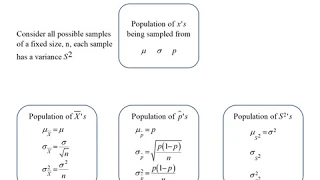
Sampling distribution parameters
How to calculate the mean, standard deviation and variance of sampling distributions for the sample mean, proportion and variance.
From playlist Exam 1 material
Gibbs Sampling : Data Science Concepts
Another MCMC Method. Gibbs sampling is great for multivariate distributions where conditional densities are *easy* to sample from. To emphasize a point in the video: - First sample is (x0,y0) - Next Sample is (x1,y1) - Next Sample is (x2,y2) ... That is, we update *all* variables once
From playlist Bayesian Statistics